A Network Pharmacology-Based Identification Study on the Mechanism of Xiao-Xu-Ming Decoction for Cerebral Ischemic Stroke
- PMID: 33133212
- PMCID: PMC7593742
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/2507074
A Network Pharmacology-Based Identification Study on the Mechanism of Xiao-Xu-Ming Decoction for Cerebral Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
Objective: We used the network pharmacological analysis method to explore the mechanism of multicomponent, multitarget, and multiway actions of Xiao-Xu-Ming decoction (XXMD) for cerebral ischemic stroke (CIS), which provided a basis on the research of innovative drugs.
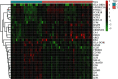
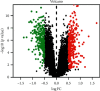
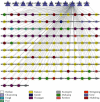
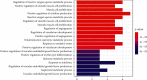
Method: We used the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform (TCMSP) to retrieve the active ingredients and targets of 12 herbs of XXMD; we used the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) to screen for differentially expressed genes in CIS to obtain the disease targets of CIS and to intersect it with the action targets of XXMD, and then the target drug efficacy is obtained. We used Cytoscape 3.6 software to construct the drug-active ingredient-action target interaction network of XXMD to treat CIS and conduct protein-protein interaction (PPI) network and topology analysis. The action target Gene Ontology (GO) biological processes and metabolic pathways in Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) of XXMD to treat CIS were enrichment analyzed with R software.
Result: We screened out 226 active ingredients and 3646 action targets for XXMD. Among them, XXMD to treat CIS has 144 active ingredients, 12 targets, and proteins in the core network of PPI having STAT3, HIF1A, etc. Pathway enrichment analysis was based on the GO and KEGG biological processes involved in active oxygen metabolism, smooth muscle cell proliferation, cytokine production, angiogenesis, redox coenzyme metabolism, and oxidative stress. The main action processes are significantly associated with CIS signal pathways involved in microRNAs, ovarian steroid hormones, NF-кB signaling pathway, Th17 cell differentiation pathway, HIF-1 signaling pathway, folic acid synthesis pathway, galactose metabolism, and fructose and mannose metabolism.
Conclusion: This study initially clarified the main targets and pathways of XXMD in the treatment of CIS, which can lay the foundation for further research on its pharmacological effects.
Copyright © 2020 De-Hui Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Emergency Medical Quality Control Center of National Health and Health Commission, Emergency Physicians Branch of Chinese Medical Association, and Emergency Committee of World Federation of Chinese Medicine Societies. Expert consensus on emergency diagnosis and treatment of acute ischemic stroke in China. Chinese Journal of Critical Care Medicine. 2018;38(4):281–287.
-
- Meng W. T., Li D. X., Tong L. Progress in research of the treatment of ischemic stroke. Chinese Journal of New Drugs. 2016;25(10):1114–1120.
-
- Liu S., Wang H. T., Wei C., et al. Advances in mechanisms of Tongxinluo capsule in treatment of ischemic stroke. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs. 2017;48(11):2321–2326.
-
- Ji S., Zhang J. P., Lv S. C., et al. On the prevention and treatment of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury with traditional Chinese medicine from Xuanfu theory. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 2013;54(14):1197–1199.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

