Predictive value of T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for the prognosis of patients with mass-type breast cancer with peritumoral edema
- PMID: 33133250
- PMCID: PMC7590426
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2020.12177
Predictive value of T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for the prognosis of patients with mass-type breast cancer with peritumoral edema
Abstract
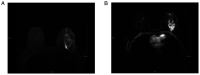
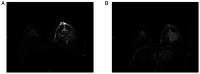
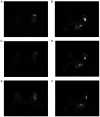
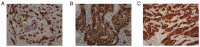
The aim of the present study was to investigate the role of edema surrounding breast cancer masses in the prognostic prediction of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) T2-weighted fat suppression sequence. For this purpose, 80 patients with mass-type breast cancer underwent conventional plain breast MRI, dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE)-MRI or diffusion-weighted MRI scan. The associations between edema around the mass on MRI T2 fat suppression sequence plain scan and tumor stage, pathological findings, immunohistochemical findings and axillary lymph node metastasis were analyzed. The results revealed the presence of edema around the mass on the MRI T2 fat suppression sequence plain scan in 35 patients. By contrast, there was no abnormal enhancement on the DCE-MRI, and the apparent diffusion coefficient value did not decrease in these areas. Compared with the remaining 45 patients, the 35 patients with peritumoral edema exhibited a higher tumor stage and a higher rate of axillary lymph node metastasis (all P<0.05). However, there was no significant difference in pathological classification or the expression of estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (as determined by immunohistochemistry) between the two groups. In total, 12 cases of tumor shrinkage during neoadjuvant chemotherapy were accompanied by an improvement in edema. Taken together, the findings of the present study indicated that the presence of edema around the mass on the MRI T2 fat suppression sequence may predict poor prognosis in patients with mass-type breast cancer. Furthermore, the improvement of the peritumoral edema post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy may also be a predictor of a more favorable prognosis.
Keywords: breast cancer; edema; magnetic resonance imaging; predictive value; prognosis.
Copyright: © Liang et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Peritumoral Fat Content Identified Using Iterative Decomposition of Water and Fat with Echo Asymmetry and Least-squares Estimation (IDEAL) Correlates with Breast Cancer Prognosis.Magn Reson Med Sci. 2025 Jan 1;24(1):112-121. doi: 10.2463/mrms.mp.2023-0127. Epub 2024 Feb 7. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 38325834 Free PMC article.
-
Is evaluation of the presence of prepectoral edema on T2-weighted with fat-suppression 3 T breast MRI a simple and readily available noninvasive technique for estimation of prognosis in patients with breast cancer?Breast Cancer. 2014 Nov;21(6):684-92. doi: 10.1007/s12282-013-0440-z. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Breast Cancer. 2014. PMID: 23341125
-
Impact of Machine Learning With Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Breast for Early Prediction of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Survival Outcomes in Breast Cancer Patients.Invest Radiol. 2019 Feb;54(2):110-117. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000518. Invest Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30358693 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction and prognosis of biologically aggressive breast cancers by the combination of DWI/DCE-MRI and immunohistochemical tumor markers.Discov Med. 2019 Jan;27(146):7-15. Discov Med. 2019. PMID: 30695671 Review.
-
Current and Emerging Therapies for HER2-Positive Women With Metastatic Breast Cancer.J Adv Pract Oncol. 2017 Mar;8(2):164-168. Epub 2017 Mar 1. J Adv Pract Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29900024 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of peritumoral region features assessed on breast MRI and prognosis of breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2024 Sep;34(9):6108-6120. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-10612-y. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38334760
-
Predicting of axillary lymph node metastasis in invasive breast cancer using multiparametric MRI dataset based on CNN model.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 6;12:1069733. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1069733. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36561533 Free PMC article.
-
The Breast Edema Enigma: Features, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Recommendations.Cureus. 2022 Apr 3;14(4):e23797. doi: 10.7759/cureus.23797. eCollection 2022 Apr. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35518543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential of predictive and prognostic breast MRI (P2-bMRI).Eur Radiol Exp. 2022 Aug 22;6(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s41747-022-00291-z. Eur Radiol Exp. 2022. PMID: 35989400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantifying tumor morphological complexity based on pretreatment MRI fractal analysis for predicting pathologic complete response and survival in breast cancer: a retrospective, multicenter study.Breast Cancer Res. 2025 May 20;27(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13058-025-02034-5. Breast Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40394616 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moschetta M, Telegrafo M, Rella L, Capolongo A, Ianora AA, Angelelli G. MR evaluation of breast lesions obtained by diffusion-weighted imaging with background body signal suppression(DWIBS) and correlations with histological findings. Magn Reson Imaging. 2014;32:605–609. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2014.03.009. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
