Predictor of respiratory disturbances during gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection under deep sedation
- PMID: 33133374
- PMCID: PMC7579530
- DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v12.i10.378
Predictor of respiratory disturbances during gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection under deep sedation
Abstract
Background: Sedation is commonly performed for the endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) of early gastric cancer. Severe hypoxemia occasionally occurs due to the respiratory depression during sedation.
Aim: To establish predictive models for respiratory depression during sedation for ESD.
Methods: Thirty-five adult patients undergoing sedation using propofol and pentazocine for gastric ESDs participated in this prospective observational study. Preoperatively, a portable sleep monitor and STOP questionnaires, which are the established screening tools for sleep apnea syndrome, were utilized. Respiration during sedation was assessed by a standard polysomnography technique including the pulse oximeter, nasal pressure sensor, nasal thermistor sensor, and chest and abdominal respiratory motion sensors. The apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) was obtained using a preoperative portable sleep monitor and polysomnography during ESD. A predictive model for the AHI during sedation was developed using either the preoperative AHI or STOP questionnaire score.
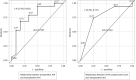
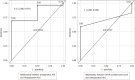
Results: All ESDs were completed successfully and without complications. Seventeen patients (49%) had a preoperative AHI greater than 5/h. The intraoperative AHI was significantly greater than the preoperative AHI (12.8 ± 7.6 events/h vs 9.35 ± 11.0 events/h, P = 0.049). Among the potential predictive variables, age, body mass index, STOP questionnaire score, and preoperative AHI were significantly correlated with AHI during sedation. Multiple linear regression analysis determined either STOP questionnaire score or preoperative AHI as independent predictors for intraoperative AHI ≥ 30/h (area under the curve [AUC]: 0.707 and 0.833, respectively) and AHI between 15 and 30/h (AUC: 0.761 and 0.778, respectively).
Conclusion: The cost-effective STOP questionnaire shows performance for predicting abnormal breathing during sedation for ESD that was equivalent to that of preoperative portable sleep monitoring.
Keywords: Deep sedation; Endoscopic submucosal dissection; Polysomnography; Respiratory depression; STOP questionnaire; Sleep apnea syndrome.
©The Author(s) 2020. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Oka S, Tanaka S, Kaneko I, Mouri R, Hirata M, Kawamura T, Yoshihara M, Chayama K. Advantage of endoscopic submucosal dissection compared with EMR for early gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;64:877–883. - PubMed
-
- Abraham NS, Fallone CA, Mayrand S, Huang J, Wieczorek P, Barkun AN. Sedation vs no sedation in the performance of diagnostic upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: a Canadian randomized controlled cost-outcome study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99:1692–1699. - PubMed
-
- Cohen LB, Delegge MH, Aisenberg J, Brill JV, Inadomi JM, Kochman ML, Piorkowski JD, Jr AGA Institute. AGA Institute review of endoscopic sedation. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:675–701. - PubMed
-
- Riphaus A, Wehrmann T, Weber B, Arnold J, Beilenhoff U, Bitter H, von Delius S, Domagk D, Ehlers AF, Faiss S, Hartmann D, Heinrichs W, Hermans ML, Hofmann C, In der Smitten S, Jung M, Kähler G, Kraus M, Martin J, Meining A, Radke J, Rösch T, Seifert H, Sieg A, Wigginghaus B, Kopp I Sektion Enoskopie im Auftrag der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Verdauungs- und Stoffwechselerkrankungen e. V. (DGVS); Bundesverband Niedergelassener Gastroenterologen Deuschlands e. V. (Bng); Chirurgische Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Endoskopie und Sonographie der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Allgemein- und Viszeralchirurgie (DGAV); Deutsche Morbus Crohn/Colitis ulcerosa Vereinigung e. V. (DCCV); Deutsche Gesellschaft für Endoskopie-Assistenzpersonal (DEGEA); Deutsche Gesellschaft für Anästhesie und Intensivmedizin (DGAI); Gesellschaft für Recht und Politik im Gesundheitswesen (GPRG). [S3-guidelines--sedation in gastrointestinal endoscopy] Z Gastroenterol. 2008;46:1298–1330. - PubMed
-
- Cohen LB, Wecsler JS, Gaetano JN, Benson AA, Miller KM, Durkalski V, Aisenberg J. Endoscopic sedation in the United States: results from a nationwide survey. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:967–974. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

