Minimally invasive vs open pancreatectomy for nonfunctioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors
- PMID: 33133382
- PMCID: PMC7579734
- DOI: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i10.1133
Minimally invasive vs open pancreatectomy for nonfunctioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors
Abstract
Background: The mainstay of treating nonfunctioning-pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors(NF-PNETs) is surgical resection. However, minimally invasive approaches to pancreatic resection for treating NF-PNETs are not widely accepted, and the long-term oncological outcomes of such approaches remain unknown.
Aim: To determine the short- and long-term outcomes of minimally invasive pancreatic resection conducted in patients with NF-PNETs.
Methods: Prospective databases from Severance Hospital were searched for 110 patients who underwent curative resection for NF-PNETs between January 2003 and August 2018.
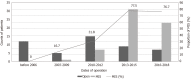
Results: The proportion of minimally invasive surgery (MIS) procedures performed for NF-PNET increased to more than 75% after 2013. There was no significant difference in post-operative complications (P = 0.654), including pancreatic fistula (P = 0.890) and delayed gastric emptying (P = 0.652), between MIS and open approaches. No statistically significant difference was found in disease-free survival between the open approach group and the MIS group (median follow-up period, 28.1 mo; P = 0.428). In addition, the surgical approach (MIS vs open) was not found to be an independent prognostic factor in treating NF-PNET patients [Exp(β) = 1.062; P = 0.929].
Conclusion: Regardless of the type of surgery, a minimally invasive approach can be safe and feasible for select NF-PNET patients.
Keywords: Laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy; Laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy; Minimally invasive surgery; Nonfunctioning-pancreas neuroendocrine tumor; Oncologic outcome; Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor.
©The Author(s) 2020. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no potential financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Minimally Invasive Versus Open Pancreatectomy for Right-Sided and Left-Sided G1/G2 Nonfunctioning Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Multicenter Matched Analysis with an Inverse Probability of Treatment-Weighting Method.Ann Surg Oncol. 2021 Nov;28(12):7742-7758. doi: 10.1245/s10434-021-10092-0. Epub 2021 May 9. Ann Surg Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33969463
-
The clinicopathologic and operative characteristics of patients with small nonfunctioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.ANZ J Surg. 2021 Jul;91(7-8):E484-E492. doi: 10.1111/ans.17055. Epub 2021 Jul 21. ANZ J Surg. 2021. PMID: 34291544
-
Laparoscopic versus open distal pancreatectomy for nonfunctioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: a large single-center study.Surg Endosc. 2018 Jan;32(1):443-449. doi: 10.1007/s00464-017-5702-y. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Surg Endosc. 2018. PMID: 28664429
-
Minimally Invasive Techniques for Resection of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors.Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2016 Jan;25(1):195-215. doi: 10.1016/j.soc.2015.08.009. Epub 2015 Oct 31. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2016. PMID: 26610782 Review.
-
Surgical resection of neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas (pNETs) by minimally invasive surgery: the laparoscopic approach.Gland Surg. 2018 Feb;7(1):12-19. doi: 10.21037/gs.2017.11.06. Gland Surg. 2018. PMID: 29629315 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Robotic Versus Laparoscopic Versus Open Surgery for Non-Metastatic Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors (pNETs): A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 22;13(21):6303. doi: 10.3390/jcm13216303. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39518444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contemporary Approaches to the Surgical Management of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 14;16(8):1501. doi: 10.3390/cancers16081501. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38672582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Outcomes of Minimally Invasive Versus Open Pancreatoduodenectomy in Distal Cholangiocarcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2024 Apr 30;16(4):e59404. doi: 10.7759/cureus.59404. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38817514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Similar Outcomes in Minimally Invasive versus Open Management of Primary Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Regional, Multi-Institutional Collaborative Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 9;14(6):1387. doi: 10.3390/cancers14061387. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326539 Free PMC article.
-
Minimally invasive versus open surgery for nonfunctioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2024 Dec 1;110(12):8250-8255. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002143. Int J Surg. 2024. PMID: 39806757 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson CW, Bennett JJ. Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2016;25:363–374. - PubMed
-
- Hill JS, McPhee JT, McDade TP, Zhou Z, Sullivan ME, Whalen GF, Tseng JF. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: the impact of surgical resection on survival. Cancer. 2009;115:741–751. - PubMed
-
- Kang CM, Kim KS, Choi JS, Lee WJ, Kim BR. Experiences with nonfunctioning neuroendocrine neoplasms of the pancreas. Dig Surg. 2005;22:453–458. - PubMed
-
- Cienfuegos JA, Salguero J, Núñez-Córdoba JM, Ruiz-Canela M, Benito A, Ocaña S, Zozaya G, Martí-Cruchaga P, Pardo F, Hernández-Lizoáin JL, Rotellar F. Short- and long-term outcomes of laparoscopic organ-sparing resection in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: a single-center experience. Surg Endosc. 2017;31:3847–3857. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

