Prognostic factors and therapeutic effects of different treatment modalities for colorectal cancer liver metastases
- PMID: 33133385
- PMCID: PMC7579728
- DOI: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i10.1177
Prognostic factors and therapeutic effects of different treatment modalities for colorectal cancer liver metastases
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common malignant tumors in China, and the liver is the most common metastatic site in patients with advanced CRC. Hepatectomy is the gold standard treatment for colorectal liver metastases. For patients who cannot undergo radical resection of liver metastases for various reasons, ablation therapy, interventional therapy, and systemic chemotherapy can be used to improve their quality of life and prolong their survival time.
Aim: To explore the prognostic factors and treatments of liver metastases of CRC.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 87 patients with liver metastases from CRC treated at the Liaoning Cancer Hospital and Institute between January 2005 and March 2011. According to different treatments, the patients were divided into the following four groups: Surgical resection group (36 patients); ablation group (23 patients); intervention group (15 patients); and drug group (13 patients). The clinicopathological data and postoperative survival of the four groups were analyzed. The Kaplan-Meier method was used for survival analysis, and the Cox proportional hazards regression model was used for multivariate analysis.
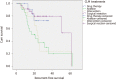
Results: The median survival time of the 87 patients was 38.747 ± 3.062 mo, and the 1- and 3-year survival rates were 87.5% and 53.1%, respectively. The Cox proportional hazards model showed that the following factors were independent factors affecting prognosis: The degree of tumor differentiation, the number of metastases, the size of metastases, and whether the metastases are close to great vessels. The results of treatment factor analysis showed that the effect of surgical treatment was better than that of drugs, intervention, or ablation alone, and the median survival time was 48.83 ± 4.36 mo. The drug group had the worst prognosis, with a median survival time of only 13.5 ± 0.7 mo (P < 0.05). For patients with liver metastases of CRC near the great vessels, the median survival time (27.3 mo) of patients undergoing surgical resection was better than that of patients using other treatments (20.6 mo) (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Patients with a low degree of primary tumor differentiation, multiple liver metastases (number of tumors > 4), and maximum diameter of liver metastases > 5 cm have a poor prognosis. Among drug therapy, intervention, ablation, and surgical treatment options, surgical treatment is the first choice for liver metastases. When liver metastases are close to great vessels, surgical treatment is significantly better than drug therapy, intervention, and ablation alone.
Keywords: Ablation; Colorectal cancer; Liver metastasis; Prognostic factors; Retrospective study; Surgical resection.
©The Author(s) 2020. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no potential financial interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
[Comparative study of ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation and surgical resection for colorectal cancer with liver metastasis].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Mar 10;100(9):696-701. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2020.09.010. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32187914 Chinese.
-
[Prognostic factors for long-term outcome of hepatic resection for colorectal liver metastases].Chir Ital. 2005 Sep-Oct;57(5):555-70. Chir Ital. 2005. PMID: 16241086 Italian.
-
[Prognostic analysis of 220 colorectal cancer patients with synchronous liver metastases].Ai Zheng. 2006 Sep;25(9):1153-7. Ai Zheng. 2006. PMID: 16965661 Chinese.
-
Prognostic Factors after Liver Resection for Colorectal Liver Metastasis.Acta Med Port. 2015 May-Jun;28(3):357-69. doi: 10.20344/amp.4816. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Acta Med Port. 2015. PMID: 26421789 Review.
-
Recent Advance in the Surgical Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer-An English Version.J Anus Rectum Colon. 2022 Oct 27;6(4):213-220. doi: 10.23922/jarc.2022-048. eCollection 2022. J Anus Rectum Colon. 2022. PMID: 36348943 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Contrast MR-Based Radiomics and Machine Learning Analysis to Assess Clinical Outcomes following Liver Resection in Colorectal Liver Metastases: A Preliminary Study.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Feb 22;14(5):1110. doi: 10.3390/cancers14051110. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35267418 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and interpretation of weight-balanced enhanced machine learning models for predicting liver metastasis risk in colorectal cancer patients.Discov Oncol. 2025 Feb 12;16(1):164. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-01871-2. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39937330 Free PMC article.
-
The predictive value of galectin-1 and vascular mimicry in the prognostic evaluation of patients with rectal cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2021 Mar;10(3):1500-1508. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-121. Transl Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35116475 Free PMC article.
-
Nomograms for predicting overall survival in colorectal cancer patients with metastasis to the liver, lung, bone, and brain.Cancer Causes Control. 2023 Dec;34(12):1059-1072. doi: 10.1007/s10552-023-01744-5. Epub 2023 Jul 24. Cancer Causes Control. 2023. PMID: 37486401
-
Bisphosphonate-mineralized nano-IFNγ suppresses residual tumor growth caused by incomplete radiofrequency ablation through metabolically remodeling tumor-associated macrophages.Theranostics. 2025 Jan 1;15(3):1057-1076. doi: 10.7150/thno.100998. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 39776793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–132. - PubMed
-
- Du LB, Li HZ, Wang YQ, Zhu C, Zheng RS, Zhang SW, Chen WQ, He J. [Report of colorectal cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2013] Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2017;39:701–706. - PubMed
-
- Fonseca GM, Herman P, Faraj SF, Kruger JAP, Coelho FF, Jeismann VB, Cecconello I, Alves VAF, Pawlik TM, de Mello ES. Pathological factors and prognosis of resected liver metastases of colorectal carcinoma: implications and proposal for a pathological reporting protocol. Histopathology. 2018;72:377–390. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

