Robotic-Assisted Knee Arthroplasty (RAKA): The Technique, the Technology and the Transition
- PMID: 33133397
- PMCID: PMC7572961
- DOI: 10.1007/s43465-020-00088-5
Robotic-Assisted Knee Arthroplasty (RAKA): The Technique, the Technology and the Transition
Abstract
Background: There has been an exponential increase in knee arthroplasty over the past 20 years. This has led to a quest for improvement in outcomes and patient satisfaction. While the last decade of last century proved to be the decade for Computer-Assisted Surgery (CAS) or Computer Navigation wherein the technology demonstrated a clear benefit in terms of improving mechanical axis alignment and component positioning, this decade is likely to belong to Robotics. Robotics adds an independent dimension to the benefits that CAS offers. The article deals with the generation of robots, technical steps in robotics, advantages and downsides of robotics and way forward in the field of knee arthroplasty.
Materials and methods: The review article was designed and edited by six different authors reviewing 32 relevant pubmed-based articles related to robotics in arthroplasty and orthopaedics. The concept, design and the definition of the intellectual content were based on the internationally published literature and insightful articles. The review is also based on the clinical experimental studies published in the literature.
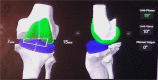
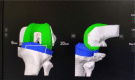
Discussion: The robotic arm is actively involved with surgeon to achieve the precision and outcomes that the surgeon aims for. With the concept of haptic boundaries and augmented reality being incorporated in most systems, Robotic Assisted Arthroplasty (RAA) is likely to offer several advantages. The potential advantages of these systems may include accuracy in gap balancing, component positioning, minimal bone resection, reduced soft tissue handling and trauma, patient anatomy specific resection, and real time feedback. They, however, come with their own downsides in terms of capital cost, learning curve, time consumption and unclear advantages in term of long-term clinical outcomes.
Conclusion: To conclude, this review article offers a balanced view on how the technology is impacting current arthroplasty practice and what can be expected in coming years. The commitment of almost all major implant manufacturers in investing in robotics likely means that the evolution of Robotic technology and this decade will be exciting with rapid strides revealing paradigm shift and evolution of technology with significant reductions of cost enabling it to be available universally. For technology to populate in operating room, I think it will be result of exposure of young surgeons to these computers and robotics, as they grow in with confidence with technology from residency days to offer better precision in future.
Keywords: Alignment; Component positioning; Computer assisted surgery (CAS); Knee arthroplasty; Robotic arthroplasty; Robotic surgery; Robotic-assisted knee arthroplasty (RAKA); UKR.
© Indian Orthopaedics Association 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestNone.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Technological innovations in shoulder replacement: current concepts and the future of robotics in total shoulder arthroplasty.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2023 Oct;32(10):2161-2171. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2023.04.022. Epub 2023 May 30. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2023. PMID: 37263482 Review.
-
Latest Advances in Robot-Assisted Knee Arthroplasty.Surg Technol Int. 2021 Oct 26;39:331-337. doi: 10.52198/21.STI.39.OS1423. Surg Technol Int. 2021. PMID: 34699601
-
Robotics in Arthroplasty: A Comprehensive Review.J Arthroplasty. 2016 Oct;31(10):2353-63. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2016.05.026. Epub 2016 May 18. J Arthroplasty. 2016. PMID: 27325369 Review.
-
Robotic-assisted knee arthroplasty.Expert Rev Med Devices. 2015;12(6):727-35. doi: 10.1586/17434440.2015.1086264. Epub 2015 Sep 12. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2015. PMID: 26365088 Review.
-
Computer-assisted hip and knee arthroplasty. Navigation and active robotic systems: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2004;4(2):1-39. Epub 2004 Feb 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2004. PMID: 23074452 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The role of next-generation robotic systems in transforming knee arthroplasty: precision and beyond.J Robot Surg. 2025 Jul 15;19(1):393. doi: 10.1007/s11701-025-02560-6. J Robot Surg. 2025. PMID: 40664971 Review.
-
The landscape of surgical robotics in orthopedics surgery.Biomed Eng Lett. 2023 Oct 11;13(4):537-542. doi: 10.1007/s13534-023-00321-8. eCollection 2023 Nov. Biomed Eng Lett. 2023. PMID: 37873001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pitfalls with the MAKO Robotic-Arm-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Feb 2;60(2):262. doi: 10.3390/medicina60020262. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38399549 Free PMC article.
-
Augmented Intelligence in Joint Replacement Surgery: How can artificial intelligence (AI) bridge the gap between the man and the machine?Arthroplasty. 2022 Feb 2;4(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s42836-021-00108-1. Arthroplasty. 2022. PMID: 35236504 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of economic and healthcare resource utilization outcomes for robotic versus manual total knee arthroplasty.J Robot Surg. 2023 Dec;17(6):2899-2910. doi: 10.1007/s11701-023-01703-x. Epub 2023 Oct 11. J Robot Surg. 2023. PMID: 37819597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Orthopedic Network News. (2013). Hip and knee implant review. Available at: http://www.OrthopedicNetworkNews.com.
-
- MDDI Online. MDDI Online. (2020). Available from: https://www.mddionline.com/. Cited Feb 21, 2020
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
