To do or not to do: prolapsed, bleeding, rectal polyp, a dilemma in austere circumstances
- PMID: 33133504
- PMCID: PMC7588305
- DOI: 10.1093/jscr/rjaa400
To do or not to do: prolapsed, bleeding, rectal polyp, a dilemma in austere circumstances
Abstract
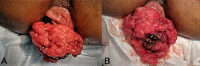
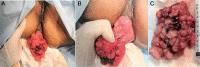
Polyps are defined as abnormal growth of tissue from a mucosal surface. Rectal polyps are the most common (2%) cause of gastro-intestinal bleed in children below 10 years. In adults, a rectal polyp presenting as an emergency with irreducible prolapse and massive bleeding causing severe anemia is seldom seen. We present one such case in which surgery was performed under austere circumstances before any investigations, as a life saving measure.
Keywords: austere circumstances; rectal polyp; rectal prolapse; tubulo-villous adenoma.
Published by Oxford University Press and JSCR Publishing Ltd. All rights reserved. © The Author(s) 2020.
Figures
References
-
- Pohl J, Schmidt H. Solitary juvenile polyp. Video J Encyclopedia GI Endosc 2013;410–1.
-
- Sardinas C, Díaz D, Oropeza ME, Parrella M, Merheb M. Rectal prolapse due to adenomatous polyp: case report. J Hepatol Gastroint Dis 2016;2:4.
-
- Garrett KA, Lee SW. Chapter V, The ASCRS Textbook of Colon and Rectal Surgery, 3rd edn. Springer Publications.
-
- Shah PR, Joseph A, Haray PN, Kiberu S. Giant villous adenoma in an incarcerated rectal prolapse: a clinical conundrum! Indian J Surg 2005;67:100–1.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

