Sichuan paocai fermented by mixed-starter culture of lactic acid bacteria
- PMID: 33133542
- PMCID: PMC7590268
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.1833
Sichuan paocai fermented by mixed-starter culture of lactic acid bacteria
Abstract
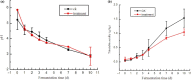
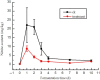
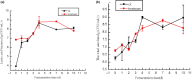
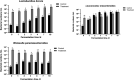
To satisfy the demand of industrial production, selecting strains suitable for fermentation initiation is necessary. In this study, the effects of mixed-starter culture including Leuconostoc, Lactobacillus, and Weissella on the quality of Sichuan pickle were discussed. Results showed that mixed-starter culture can accelerate fermentation and had the highest efficiency for nitrite degradation, that is, the maximum nitrite concentration was 8.97 g/kg on day 1 and decreased to 1.88 mg/kg after 3 days. The mixed-starter culture improved the sensory properties of pickles, which easily produced acids but had reduced amounts of total acids. The pickle products fermented by the mixed-starter culture contained increased lactic acid (17.52 g/kg), mannitol (0.62%), umami (35.85), and sweet (11.36) amino acids on day 4. The strains Weissella paramesenteroides C2-2 and Lactobacillus brevis ZP11-2 grew well in the mixed-starter culture fermentation.
Keywords: Brassica juncea var. tumida Tsen; Lactobacillus; Leuconostoc; Sichuan paocai; Weissella; mixed‐starter culture.
© 2020 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors hereby declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Choi, I. , Jung, S. , Kim, B. , Park, S. , Kim, J. , & Han, H. (2003). Novel Leuconostoc citreum starter culture system for the fermentation of kimchi, a fermented cabbage product. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 84(4), 247–253. - PubMed
-
- Çon, A. , & Karasu, N. (2009). Determination of antagonistic starter cultures for pickle and olive fermentation processes. Czech Journal of Food Sciences, 27(3), 185–193. 10.17221/86/2008-CJFS - DOI
-
- Gao, Y. , Li, D. , & Liu, X. (2014). Bacteriocin‐producing Lactobacillus sakei C2 as starter culture in fermented sausages. Food Control, 35(1), 1–6.
-
- Grobben, G. , Peters, S. , Wisselink, H. , Weusthuis, R. , Hoefnagel, M. , Hugenholtz, J. , & Eggink, G. (2001). Spontaneous formation of a mannitol‐producing variant of Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides grown in the presence of fructose. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67(6), 2867–2870. 10.1128/AEM.67.6.2867-2870.2001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jung, J. , Lee, S. , Lee, H. , Seo, H. , Park, W. , & Jeon, C. (2012). Effects of Leuconostoc mesenteroides starter cultures on microbial communities and metabolites during kimchi fermentation. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 153(3), 378–387. 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.11.030 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

