Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases with IL-1 Blockade
- PMID: 33133777
- PMCID: PMC7597638
- DOI: 10.1007/s40136-018-0181-9
Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases with IL-1 Blockade
Abstract
Background: Autoinflammatory diseases are distinct from autoimmune diseases. Whereas autoinflammatory diseases are due to dysfunctional T-cells and B-cells, autoinflammatory diseases are due to overproduction of macrophage cytokines particularly interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β). A causative role for IL-1 in autoinflammatory diseases is derived from clinical studies blocking the IL-1 receptor or neutralizing monoclonal antibodies or soluble receptors.
Methods: A review was performed of clinical trials in autoinflammatory diseases using the IL-1 receptor antagonist (anakinra), the soluble IL-1 receptor (rilonacept), antibodies to IL-1β (canakinumab, gevokizumab) and anti-IL-1α (xilonix).
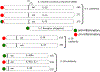
Findings: Anakinra blocks the IL-1 Receptor type 1 (IL-1R1) and therefore blocks the activities of both IL-1α and IL-1β. Off-label use of anakinra is common for a broad spectrum of inflammatory diseases. Neutralization of IL-1β is used to treat hereditary autoinflammatory diseases but also atherosclerosis. Rilonacept reduces arterial wall inflammation in patients with chronic kidney disease. Neutralization of IL-1α has prolonged life in patients with advanced metastatic colorectal cancer. Compared to other cytokine blocking therapies, reducing the activities of IL-1 has an excellent safety record.
Conclusions: Blocking IL-1 therapies can be used to treat a wide-spectrum of acute and chronic inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: anakinra; canakinumab; cancer; innate immunity; rilonacept; xilonix.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treating inflammation by blocking interleukin-1 in humans.Semin Immunol. 2013 Dec 15;25(6):469-84. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2013.10.008. Epub 2013 Nov 23. Semin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24275598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treating rheumatological diseases and co-morbidities with interleukin-1 blocking therapies.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015 Dec;54(12):2134-44. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev269. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015. PMID: 26209330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anakinra Therapy for Non-cancer Inflammatory Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Nov 6;9:1157. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01157. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30459597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-1 Blockade in Polygenic Autoinflammatory Disorders: Where Are We now?Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 26;11:619273. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.619273. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33708123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic Review of Safety and Efficacy of IL-1-Targeted Biologics in Treating Immune-Mediated Disorders.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 6;13:888392. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.888392. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35874710 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Systemic inflammation as a biomarker of seizure propensity and a target for treatment to reduce seizure propensity.Epilepsia Open. 2023 Mar;8(1):221-234. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12684. Epub 2023 Jan 23. Epilepsia Open. 2023. PMID: 36524286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory Property of AMP-activated Protein Kinase.Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2020;19(1):2-41. doi: 10.2174/1871523018666190830100022. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31530260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Key Factor Regulating Inflammatory Microenvironment, Metastasis, and Resistance in Breast Cancer: Interleukin-1 Signaling.Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Sep 23;2021:7785890. doi: 10.1155/2021/7785890. eCollection 2021. Mediators Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 34602858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Inflammatory Mediators in Epilepsy: A Systematic Review of Its Molecular Basis and Clinical Applications.Front Neurol. 2022 Mar 11;13:741244. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.741244. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35359659 Free PMC article.
-
Rational Design of Inner Ear Drug Delivery Systems.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Aug;12(29):e2410568. doi: 10.1002/advs.202410568. Epub 2025 May 8. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40344640 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Drenth JP, van der Meer JW, Kushner I. Unstimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with the hyper-IgD syndrome produce cytokines capable of potent induction of C-reactive protein and serum amyloid A in Hep3B cells. J Immunol 1996;157(1):400–4. - PubMed
-
- Gattorno M, Piccini A, Lasiglie D, Tassi S, Brisca G, Carta S, et al. The pattern of response to anti-interleukin-1 treatment distinguishes two subsets of patients with systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2008;58(5):1505–15. - PubMed
-
- Gattorno M, Tassi S, Carta S, Delfino L, Ferlito F, Pelagatti MA, et al. Pattern of interleukin-1beta secretion in response to lipopolysaccharide and ATP before and after interleukin-1 blockade in patients with CIAS1 mutations. Arthritis Rheum 2007;56(9):3138–48. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
