Spatiotemporal expansion of human brucellosis in Shaanxi Province, Northwestern China and model for risk prediction
- PMID: 33133781
- PMCID: PMC7580622
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.10113
Spatiotemporal expansion of human brucellosis in Shaanxi Province, Northwestern China and model for risk prediction
Abstract
Background: Human brucellosis imposes a heavy burden on the health and economy of endemic regions. Since 2011, China has reported at least 35,000 human brucellosis cases annually, with more than 90% of these cases reported in the northern. Given the alarmingly high incidence and variation in the geographical distribution of human brucellosis cases, there is an urgent need to decipher the causes of such variation in geographical distribution.
Method: We conducted a retrospective epidemiological study in Shaanxi Province from January 1, 2005 to December 31, 2018 to investigate the association between meteorological factors and transmission of human brucellosis according to differences in geographical distribution and seasonal fluctuation in northwestern China for the first time.
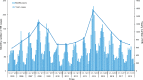
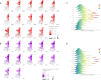
Results: Human brucellosis cases were mainly distributed in the Shaanbei upland plateau before 2008 and then slowly extended towards the southern region with significant seasonal fluctuation. The results of quasi-Poisson generalized additive mixed model (GAMM) indicated that air temperature, sunshine duration, rainfall, relative humidity, and evaporation with maximum lag time within 7 months played crucial roles in the transmission of human brucellosis with seasonal fluctuation. Compared with the Shaanbei upland plateau, Guanzhong basin had more obvious fluctuations in the occurrence of human brucellosis due to changes in meteorological factors. Additionally, the established GAMM model showed high accuracy in predicting the occurrence of human brucellosis based on the meteorological factors.
Conclusion: These findings may be used to predict the seasonal fluctuations of human brucellosis and to develop reliable and cost-effective prevention strategies in Shaanxi Province and other areas with similar environmental conditions.
Keywords: Generalized additive mixed model; Human brucellosis; Meteorological factors; Regional differences; Spatiotemporal expansion.
©2020 Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Socioeconomic, meteorological factors and spatiotemporal distribution of human brucellosis in China between 2004 and 2019-A study based on spatial panel model.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023 Nov 13;17(11):e0011765. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011765. eCollection 2023 Nov. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023. PMID: 37956207 Free PMC article.
-
Risk effects of meteorological factors on human brucellosis in Jilin province, China, 2005-2019.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 15;10(8):e29611. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29611. eCollection 2024 Apr 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38660264 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of climatic factors on the seasonal fluctuation of human brucellosis in Yulin, northern China.BMC Public Health. 2020 Apr 16;20(1):506. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-08599-4. BMC Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32299414 Free PMC article.
-
Brucellosis seroprevalence in dairy cattle in China during 2008-2018: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Acta Trop. 2019 Jan;189:117-123. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.10.002. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Acta Trop. 2019. PMID: 30308207
-
Distribution of geographical scale, data aggregation unit and period in the correlation analysis between temperature and incidence of HFRS in mainland China: A systematic review of 27 ecological studies.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Aug 19;13(8):e0007688. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007688. eCollection 2019 Aug. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 31425512 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Seroprevalence of human brucellosis among the tribal and non-tribal population residing in an eastern state of India: Findings from the state-wide serosurvey.Front Microbiol. 2022 Nov 28;13:1070276. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1070276. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36519171 Free PMC article.
-
Risk effects of environmental factors on human brucellosis in Aksu Prefecture, Xinjiang, China, 2014-2023.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 23;15(1):2908. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-86889-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39849046 Free PMC article.
-
Socioeconomic, meteorological factors and spatiotemporal distribution of human brucellosis in China between 2004 and 2019-A study based on spatial panel model.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023 Nov 13;17(11):e0011765. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011765. eCollection 2023 Nov. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023. PMID: 37956207 Free PMC article.
-
Driving role of climatic and socioenvironmental factors on human brucellosis in China: machine-learning-based predictive analyses.Infect Dis Poverty. 2023 Apr 12;12(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s40249-023-01087-y. Infect Dis Poverty. 2023. PMID: 37046326 Free PMC article.
-
Risk effects of meteorological factors on human brucellosis in Jilin province, China, 2005-2019.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 15;10(8):e29611. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29611. eCollection 2024 Apr 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38660264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cotterill GG, Cross PC, Cole EK, Fuda RK, Rogerson JD, Scurlock BM, Du Toit JT. Winter feeding of elk in the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem and its effects on disease dynamics. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2018;373(1745):20170093. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2017.0093. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

