Quality of Life in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Three Months After Laparoscopic Nissen's Fundoplication
- PMID: 33133840
- PMCID: PMC7592527
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.10674
Quality of Life in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Three Months After Laparoscopic Nissen's Fundoplication
Abstract
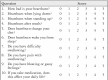
Introduction: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) affects various elements of life including sleep, daily and social functioning, and physical and emotional activities. This study aims to determine the impact of laparoscopic Nissen's fundoplication (LNF) on health-related quality of life.
Methods: This prospective study was conducted in a tertiary care hospital, Pakistan, from Jan 2019 to Feb 2020. Forty-seven participants completed the study. All patients completed the Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Health-Related Quality of Life (GERD-HRQoL) questionnaire both pre-operatively and three months after LNF.
Results: There was significant difference in pre- and post-operative median Health-Related Quality of Life score (p value: 0.0073). There was improvement in items related to heartburn in HRQoL questionnaire, while questions related to swallowing and bloating either showed no change or worsening.
Conclusion: LNF has a significant impact on health-related quality of life. It is important for the physician to consider the impact of GERD in daily life. Management goals for GERD should also include improvement in quality of life of the patient.
Keywords: gerd-hrql.
Copyright © 2020, Kumar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quality of life and patient satisfaction 3 months and 3 years after laparoscopic Nissen's fundoplication.Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2008 Jan;14(1):24-7. doi: 10.4103/1319-3767.37799. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 19568490 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of laparoscopic Nissen's fundoplication on response of disease specific symptoms and quality of life.Updates Surg. 2013 Mar;65(1):35-41. doi: 10.1007/s13304-012-0193-9. Epub 2012 Dec 30. Updates Surg. 2013. PMID: 23275254
-
Laparoscopic vs. open Nissen's fundoplication for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in children: A meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2016 Oct;34:10-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2016.08.017. Epub 2016 Aug 27. Int J Surg. 2016. PMID: 27554458
-
Effectiveness of laparoscopic fundoplication in relieving the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and eliminating antireflux medical therapy.Surg Endosc. 2003 Aug;17(8):1200-5. doi: 10.1007/s00464-002-8910-y. Epub 2003 May 13. Surg Endosc. 2003. PMID: 12739117 Review.
-
Laparoscopic magnetic sphincter augmentation versus fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease: systematic review and pooled analysis.Dis Esophagus. 2019 Nov 13;32(9):doz031. doi: 10.1093/dote/doz031. Dis Esophagus. 2019. PMID: 31069388
Cited by
-
Sorting out the Relationship between Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Sleep.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2021 Aug 2;23(9):15. doi: 10.1007/s11894-021-00815-4. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34338891 Review.
-
Chitosan Nanoparticles for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Treatment.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Aug 20;15(16):3485. doi: 10.3390/polym15163485. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631542 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Risk factors and prescription patterns of gastroesophageal reflux disease: HEAL study in Pakistan. Butt AK, Hashmey I. https://jpma.org.pk/article-details/6826. J Pak Med Assoc. 2014;64:751–757. - PubMed
-
- The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidence-based consensus. Vakil N, Zanten SV, Kahrilas P, Dent J, Jones R. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:1900–1920. - PubMed
-
- Review of the quality of life and burden of illness in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Wiklund I. Dig Dis. 2004;22:108–114. - PubMed
-
- Controversies in long-term management of reflux disease. Dent J. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2000;14:811–826. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources