Novel Technique with Double Free Flap Design for Advanced Mandibular Osteoradionecrosis: A Case Series
- PMID: 33133983
- PMCID: PMC7544289
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000003149
Novel Technique with Double Free Flap Design for Advanced Mandibular Osteoradionecrosis: A Case Series
Abstract
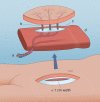
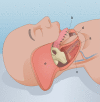
Advanced mandibular osteoradionecrosis is arguably among the most challenging cases for reconstructive head and neck surgeons. Several reconstructive methods for complex mandibular defects have been reported; however, for advanced mandibular osteoradionecrosis, a safe option that minimizes the risk of renewed fistulation and infections is needed. For this purpose, we present a new technique using a fascia-sparing vertical rectus abdominis musculocutaneous flap as protection for a vascularized free fibula graft (FFG). This technique also optimizes recipient site healing and functionality while minimizing donor site morbidity. Our initial experiences from a 4 patient case series are included. Mean operative time was 551 minutes (SD: 81 minutes). All donor sites were closed primarily. Mean time to discharge was 13 days (SD: 7 days), and mean time to full mobilization was 2 days (SD: 1 days). This double free flap technique completely envelops the FFG and plate with nonirradiated muscle. It allows for the transfer of an FFG without a skin island, thus avoiding the need for split skin graft closure. This results in faster healing and minimizes the risk of fibula donor site morbidity. The skin island of the vertical rectus abdominis musculocutaneous flap has the added benefit of providing intraoral lining, which minimizes contractures and trismus. Although prospective long-term studies comparing this approach to other double flap procedures are needed, we argue that this technique is an optimal approach to safeguard the mandibular FFG reconstruction against the inherent risks of renewed complications in irradiated unhealthy tissue.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors have no financial interest to declare in relation to the content of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Osteoradionecrosis of the mandible after oromandibular cancer surgery.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002 May;109(6):1875-81. doi: 10.1097/00006534-200205000-00014. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002. PMID: 11994586
-
Minimizing osteoradionecrosis after mandibular reconstruction and radiation in advanced head and neck cancer patients.J Surg Oncol. 2016 Sep;114(4):399-404. doi: 10.1002/jso.24321. Epub 2016 Aug 22. J Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27545968
-
Management of an exposed mandibular plate after fibula free flap with vacuum-assisted closure system.J Craniofac Surg. 2011 May;22(3):905-8. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e31820f7fac. J Craniofac Surg. 2011. PMID: 21558925
-
Anterolateral thigh flap reconstruction of large external facial skin defects: a follow-up study on functional and aesthetic recipient- and donor-site outcome.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005 Apr;115(4):1077-86. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000156153.17258.ce. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005. PMID: 15793449
-
Fibula osteofascial flap with proximal skin paddle for intraoral reconstruction.Microsurgery. 2017 May;37(4):276-281. doi: 10.1002/micr.30084. Epub 2016 Jul 29. Microsurgery. 2017. PMID: 27471008
Cited by
-
Management of Radiation-induced Tissue Injuries: A Review of Current Treatment Strategies.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2023 Jun 16;11(6):e5043. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000005043. eCollection 2023 Jun. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2023. PMID: 37456134 Free PMC article.
-
The Progress in Reconstruction of Mandibular Defect Caused by Osteoradionecrosis.J Oncol. 2023 Mar 15;2023:1440889. doi: 10.1155/2023/1440889. eCollection 2023. J Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36968640 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rommel N, Kesting MR, Rohleder NH, et al. Surgical management of severe osteoradionecrosis of the mandibular bone by using double free flap reconstruction. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2018;46:148. - PubMed
-
- Park L, Lilic N, Addison B, et al. Cost analysis of osteoradionecrosis. J Laryngol Otol. 2017;131:303–308. - PubMed
-
- Zaghi S, Miller M, Blackwell K, et al. Analysis of surgical margins in cases of mandibular osteoradionecrosis that progress despite extensive mandible resection and free tissue transfer. Am J Otolaryngol. 2012;33:576–580. - PubMed
-
- Cannady SB, Dean N, Kroeker A, et al. Free flap reconstruction for osteoradionecrosis of the jaws–outcomes and predictive factors for success. Head Neck. 2011;33:424–428. - PubMed
-
- Kroll SS, Schusterman MA, Reece GP, et al. Choice of flap and incidence of free flap success. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1996;98:459–463. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
