Bio-Numerical Analysis of the Human Ankle-Foot Model Corresponding to Neutral Standing Condition
- PMID: 33134224
- PMCID: PMC7557457
- DOI: 10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.2004-1094
Bio-Numerical Analysis of the Human Ankle-Foot Model Corresponding to Neutral Standing Condition
Abstract
Background: The foot is the most complex body's structure; it is highly susceptible to disorders because of its loading pattern. The complexity of the foot structure geometry implies the use of reverse engineering tools to obtain a model that can accurately mimic the biomechanical behavior of the foot.
Objective: The objective of this study is to establish a state-of-the-art ankle-foot finite element (FE) model with anatomically realistic geometry and structure in order to get the model that will suit all cases for future studies on stress injuries and foot insole designs under different loading conditions.
Material and methods: In this analytical study, tomography images were imported in DICOM format, after that, the object was exported in the form of three-dimensional structures in STL file format to define and assemble the structures. After that, the computer simulation on numerical model was done. One-way Analysis of variance (ANOVA) test was performed, and a threshold (p<0.05) was used to indicate the significance of results.
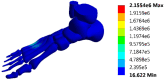
Results: The results showed no significant differences (P>0.05) between the values of the plantar pressure corresponding to neutral standing condition with other foot models in literature. The stresses transferred to the bone structure show that the relatively higher stress was located in the fifth, fourth and third tarsometatarsal, where the maximum von Mises stress in the bone structure was 2155.4 kPa.
Conclusion: The state-of-the-art ankle-foot FE model with anatomically realistic geometry and structure will be very helpful for future studies on stress injuries and foot insole designs under different loading conditions.
Keywords: Ankle; Foot; Methods; Neutral Standing; Stress Distribution.
Copyright: © Journal of Biomedical Physics and Engineering.
Figures


References
-
- Antunes P J, Dias G R, Coelho A T, Rebelo F, Pereira T. Non-linear finite element modelling of anatomically detailed 3D foot model. Report paper. 2008. p. 1 .
-
- France D L. Human and nonhuman bone identification: a color atlas. CRC Press; 2008. p. 584 .
-
- Porter D A, Schon L C. Baxter’s the Foot and Ankle in Sport. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2020. p. 624 .
-
- Abdul Razak A H, Zayegh A, Begg R K, Wahab Y. Foot plantar pressure measurement system: A review. Sensors. 2012;12(7):9884–912. doi: 10.3390/s120709884. [ PMC Free Article ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
