MicroRNA-135a Protects Against Ethanol-Induced Apoptosis in Neural Crest Cells and Craniofacial Defects in Zebrafish by Modulating the Siah1/p38/p53 Pathway
- PMID: 33134300
- PMCID: PMC7561719
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.583959
MicroRNA-135a Protects Against Ethanol-Induced Apoptosis in Neural Crest Cells and Craniofacial Defects in Zebrafish by Modulating the Siah1/p38/p53 Pathway
Abstract
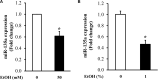
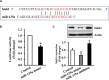
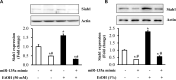
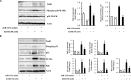
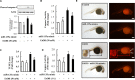
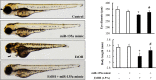
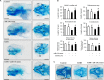
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that are involved in various biological processes, including apoptosis, by regulating gene expression. This study was designed to test the hypothesis that ethanol-induced downregulation of miR-135a contributes to ethanol-induced apoptosis in neural crest cells (NCCs) by upregulating Siah1 and activating the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/p53 pathway. We found that treatment with ethanol resulted in a significant decrease in miR-135a expression in both NCCs and zebrafish embryos. Ethanol-induced downregulation of miR-135a resulted in the upregulation of Siah1 and the activation of the p38 MAPK/p53 pathway and increased apoptosis in NCCs and zebrafish embryos. Ethanol exposure also resulted in growth retardation and developmental defects that are characteristic of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD) in zebrafish. Overexpression of miRNA-135a significantly reduced ethanol-induced upregulation of Siah1 and the activation of the p38 MAPK/p53 pathway and decreased ethanol-induced apoptosis in NCCs and zebrafish embryos. In addition, ethanol-induced growth retardation and craniofacial defects in zebrafish larvae were dramatically diminished by the microinjection of miRNA-135a mimics. These results demonstrated that ethanol-induced downregulation of miR-135a contributes to ethanol-induced apoptosis in NCCs by upregulating Siah1 and activating the p38 MAPK/p53 pathway and that the overexpression of miRNA-135a can protect against ethanol-induced apoptosis in NCCs and craniofacial defects in a zebrafish model of FASD.
Keywords: Siah1; apoptosis; craniofacial defects; ethanol; miRNA-135a; neural crest cells; zebrafish.
Copyright © 2020 Yuan, Yun, Fan, Li, Lu, Liu, Feng and Chen.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Up-regulation of microRNA-34a mediates ethanol-induced impairment of neural crest cell migration in vitro and in zebrafish embryos through modulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting Snail1.Toxicol Lett. 2022 Apr 1;358:17-26. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2022.01.004. Epub 2022 Jan 14. Toxicol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35038560 Free PMC article.
-
Neural crest cells and fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: Mechanisms and potential targets for prevention.Pharmacol Res. 2023 Aug;194:106855. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106855. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Pharmacol Res. 2023. PMID: 37460002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Up-regulation of Siah1 by ethanol triggers apoptosis in neural crest cells through p38 MAPK-mediated activation of p53 signaling pathway.Arch Toxicol. 2017 Feb;91(2):775-784. doi: 10.1007/s00204-016-1746-3. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Arch Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27270636 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-125b protects against ethanol-induced apoptosis in neural crest cells and mouse embryos by targeting Bak 1 and PUMA.Exp Neurol. 2015 Sep;271:104-11. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.04.026. Epub 2015 May 27. Exp Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26024858 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish Models of Craniofacial Malformations: Interactions of Environmental Factors.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Nov 16;8:600926. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.600926. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33304906 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sulforaphane Protects Against Ethanol-Induced Apoptosis in Human Neural Crest Cells Through Diminishing Ethanol-Induced Hypermethylation at the Promoters of the Genes Encoding the Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Feb 9;9:622152. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.622152. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33634123 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of microRNA-34a mediates ethanol-induced impairment of neural crest cell migration in vitro and in zebrafish embryos through modulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting Snail1.Toxicol Lett. 2022 Apr 1;358:17-26. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2022.01.004. Epub 2022 Jan 14. Toxicol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35038560 Free PMC article.
-
Neural crest cells and fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: Mechanisms and potential targets for prevention.Pharmacol Res. 2023 Aug;194:106855. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106855. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Pharmacol Res. 2023. PMID: 37460002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Impacts of Early Life Stress in Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Shape the Neurodevelopmental Continuum.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Jun 3;14:671891. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.671891. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34149355 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNA and Alcohol Use Disorder: A Scoping Review of Current Research and Knowledge Gaps.Alcohol Res. 2025 Jun 20;45(1):06. doi: 10.35946/arcr.v45.1.06. eCollection 2025. Alcohol Res. 2025. PMID: 40552213 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

