The Early Phase of β2-Microglobulin Aggregation: Perspectives From Molecular Simulations
- PMID: 33134317
- PMCID: PMC7550760
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.578433
The Early Phase of β2-Microglobulin Aggregation: Perspectives From Molecular Simulations
Abstract
Protein β2-microglobulin is the causing agent of two amyloidosis, dialysis related amyloidosis (DRA), affecting the bones and cartilages of individuals with chronic renal failure undergoing long-term hemodialysis, and a systemic amyloidosis, found in one French family, which impairs visceral organs. The protein's small size and its biomedical significance attracted the attention of theoretical scientists, and there are now several studies addressing its aggregation mechanism in the context of molecular simulations. Here, we review the early phase of β2-microglobulin aggregation, by focusing on the identification and structural characterization of monomers with the ability to trigger aggregation, and initial small oligomers (dimers, tetramers, hexamers etc.) formed in the so-called nucleation phase. We focus our analysis on results from molecular simulations and integrate our views with those coming from in vitro experiments to provide a broader perspective of this interesting field of research. We also outline directions for future computer simulation studies.
Keywords: dimer; docking; intermediates; molecular dynamics; native-centric simulations; protein aggregation.
Copyright © 2020 Loureiro and Faísca.
Figures
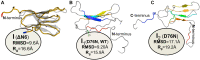
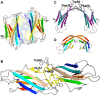
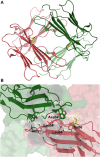
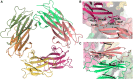
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

