Noncanonical WNT Activation in Human Right Ventricular Heart Failure
- PMID: 33134326
- PMCID: PMC7575695
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.582407
Noncanonical WNT Activation in Human Right Ventricular Heart Failure
Abstract
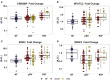
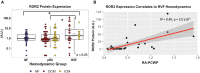
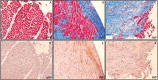
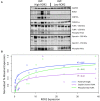
Background: No medical therapies exist to treat right ventricular (RV) remodeling and RV failure (RVF), in large part because molecular pathways that are specifically activated in pathologic human RV remodeling remain poorly defined. Murine models have suggested involvement of Wnt signaling, but this has not been well-defined in human RVF. Methods: Using a candidate gene approach, we sought to identify genes specifically expressed in human pathologic RV remodeling by assessing the expression of 28 WNT-related genes in the RVs of three groups: explanted nonfailing donors (NF, n = 29), explanted dilated and ischemic cardiomyopathy, obtained at the time of cardiac transplantation, either with preserved RV function (pRV, n = 78) or with RVF (n = 35). Results: We identified the noncanonical WNT receptor ROR2 as transcriptionally strongly upregulated in RVF compared to pRV and NF (Benjamini-Hochberg adjusted P < 0.05). ROR2 protein expression correlated linearly to mRNA expression (R 2 = 0.41, P = 8.1 × 10-18) among all RVs, and to higher right atrial to pulmonary capillary wedge ratio in RVF (R 2 = 0.40, P = 3.0 × 10-5). Utilizing Masson's trichrome and ROR2 immunohistochemistry, we identified preferential ROR2 protein expression in fibrotic regions by both cardiomyocytes and noncardiomyocytes. We compared RVF with high and low ROR2 expression, and found that high ROR2 expression was associated with increased expression of the WNT5A/ROR2/Ca2+ responsive protease calpain-μ, cleavage of its target FLNA, and FLNA phosphorylation, another marker of activation downstream of ROR2. ROR2 protein expression as a continuous variable, correlated strongly to expression of calpain-μ (R 2 = 0.25), total FLNA (R 2 = 0.67), calpain cleaved FLNA (R 2 = 0.32) and FLNA phosphorylation (R 2 = 0.62, P < 0.05 for all). Conclusion: We demonstrate robust reactivation of a fetal WNT gene program, specifically its noncanonical arm, in human RVF characterized by activation of ROR2/calpain mediated cytoskeleton protein cleavage.
Keywords: Ror2; Wnt; calpain; heart failure; remodeling; right ventricle (RV); right ventricular (RV) failure.
Copyright © 2020 Edwards, Brandimarto, Hu, Jeong, Yucel, Li, Bedi, Wada, Murashige, Hwang, Zhao, Margulies, Bernstein, Reddy and Arany.
Figures
References
-
- Babu-Narayan SV, Uebing A, Davlouros PA, Kemp M, Davidson S, Dimopoulos K, et al. . Randomised trial of ramipril in repaired tetralogy of Fallot and pulmonary regurgitation: the appropriate study (ace inhibitors for potential prevention of the deleterious effects of pulmonary regurgitation in adults with repaired tetralogy of Fallot). Int J Cardiol. (2012) 154:299–305. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2010.09.057 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Voelkel NF, Quaife RA, Leinwand LA, Barst RJ, McGoon MD, Meldrum DR, et al. Blood institute working group on, and f. molecular mechanisms of right heart, right ventricular function and failure: report of a national heart, lung, and blood institute working group on cellular and molecular mechanisms of right heart failure. Circulation. (2006) 114:1883–91. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.632208 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

