ATP-Sensitive Potassium Channels Mediate the Cardioprotective Effect of Panax notoginseng Saponins against Myocardial Ischaemia-Reperfusion Injury and Inflammatory Reaction
- PMID: 33134375
- PMCID: PMC7593753
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/3039184
ATP-Sensitive Potassium Channels Mediate the Cardioprotective Effect of Panax notoginseng Saponins against Myocardial Ischaemia-Reperfusion Injury and Inflammatory Reaction
Abstract
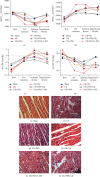
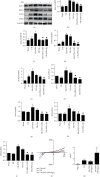
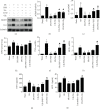
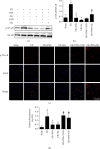
Inflammatory response during myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury (MIRI) is essential for cardiac healing, while excessive inflammation extends the infarction and promotes adverse cardiac remodeling. Understanding the mechanism of these uncontrolled inflammatory processes has a significant impact during the MIRI therapy. Here, we found a critical role of ATP-sensitive potassium channels (KATP) in the inflammatory response of MIRI and its potential mechanism and explored the effects of Panax Notoginseng Saponins (PNS) during this possess. Rats underwent 40 min ischemia by occlusion of the left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery and 60 min of reperfusion. PNS was treated at the corresponding time point before operation; 5-hydroxydecanoate (5-HD) and glybenclamide (Gly) (or Nicorandil (Nic)) were used as pharmacological blocker (or nonselective opener) of KATP. Cardiac function and pathomorphology were evaluated and a set of molecular signaling experiments was tested. KATP current density was measured by patch-clamp. Results revealed that in MIRI, PNS pretreatment restored cardiac function, reduced infarct size, and ameliorated inflammation through KATP. However, inhibiting KATP by 5-HD and Gly significantly reversed the effects, including NLRP3 inflammasome and inflammatory mediators IL-6, MPO, TNF-α, and MCP-1. Moreover, PNS inhibited the phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of NF-κB in I/R myocardium when the KATP was activated. Importantly, PNS promoted the expression of subunits and activation of KATP. The study uncovered KATP served as a new potential mechanism during PNS modulating MIRI-induced inflammation and promoting injured heart recovery. The manipulation of KATP could be a potential therapeutic approach for MIRI and other inflammatory diseases.
Copyright © 2020 Ke Ning et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
KR-31762, a novel KATP channel opener, exerts cardioprotective effects by opening SarcKATP channels in rat models of ischemia/reperfusion-induced heart injury.Arch Pharm Res. 2008 Apr;31(4):482-9. doi: 10.1007/s12272-001-1182-9. Epub 2008 May 1. Arch Pharm Res. 2008. PMID: 18449506
-
The cardioprotective effect of naringenin against ischemia-reperfusion injury through activation of ATP-sensitive potassium channel in rat.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016 Sep;94(9):973-8. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2016-0008. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27408985
-
Cholesterol-enriched diet inhibits cardioprotection by ATP-sensitive K+ channel activators cromakalim and diazoxide.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014 Feb;306(3):H405-13. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00257.2013. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24285110
-
Protective Effect of Nicorandil on Cardiac Microvascular Injury: Role of Mitochondrial Integrity.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Jul 3;2021:4665632. doi: 10.1155/2021/4665632. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. Retraction in: Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023 Oct 11;2023:9845162. doi: 10.1155/2023/9845162. PMID: 34285763 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
KATP channels are regulators of programmed cell death and targets for the creation of novel drugs against ischemia/reperfusion cardiac injury.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2023 Dec;37(6):1020-1049. doi: 10.1111/fcp.12924. Epub 2023 Jun 26. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37218378 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and safety of Panax notoginseng saponin injection in the treatment of acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 21;15:1353662. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1353662. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38576488 Free PMC article.
-
Cardio-Oncology: Mechanisms, Drug Combinations, and Reverse Cardio-Oncology.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 13;23(18):10617. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810617. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PCSK9 Knockdown Can Improve Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting Autophagy.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2022 Dec;22(12):951-961. doi: 10.1007/s12012-022-09771-5. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36342620
-
Preparation, In Vivo and In Vitro Release of Polyethylene Glycol Monomethyl Ether-Polymandelic Acid Microspheres Loaded Panax Notoginseng Saponins.Molecules. 2019 May 27;24(10):2024. doi: 10.3390/molecules24102024. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31137874 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Qualitative and Quantitative Analyses of Wenxin Granule via Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Ion Mobility Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry and Triple Quadrupole-Linear Ion Trap Mass Spectrometry.Molecules. 2022 Jun 6;27(11):3647. doi: 10.3390/molecules27113647. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35684583 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yadav M., Kumari P., Yadav V., Kumar S. Pharmacological preconditioning with phosphodiestrase inhibitor: an answer to stem cell survival against ischemic injury through JAK/STAT signaling. Heart Failure Reviews. 2019;15 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

