Orosomucoid 1 Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Cardiomyocytes via Nrf2 Signaling
- PMID: 33134382
- PMCID: PMC7591952
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/5923572
Orosomucoid 1 Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Cardiomyocytes via Nrf2 Signaling
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Orosomucoid 1 Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Cardiomyocytes via Nrf2 Signaling".Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jul 4;2022:9828942. doi: 10.1155/2022/9828942. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35832841 Free PMC article.
Abstract
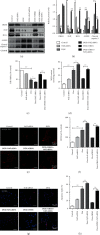
Doxorubicin (DOX) is an effective anticancer drug, but its therapeutic use is limited by its cardiotoxicity. The principal mechanisms of DOX-induced cardiotoxicity are oxidative stress and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes. Orosomucoid 1 (ORM1), an acute-phase protein, plays important roles in inflammation and ischemic stroke; however, the roles and mechanisms of ORM1 in DOX-induced cardiotoxicity remain unknown. Therefore, in the present study, we aimed to investigate the function of ORM1 in cardiomyocytes experiencing DOX-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis. A DOX-induced cardiotoxicity animal model was established in C57BL/6 mice by administering an intraperitoneal injection of DOX (20 mg/kg), and the control group was intraperitoneally injected with the same volume of sterilized saline. The effects were assessed after 7 d. Additionally, H9c2 cells were stimulated with DOX (10 μM) for 24 h. The results showed decreased ORM1 and increased oxidative stress and apoptosis after DOX stimulation in vivo and in vitro. ORM1 overexpression significantly reduced DOX-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in H9c2 cells. ORM1 significantly increased the expression of nuclear factor-like 2 (Nrf2) and its downstream protein heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1) and reduced the expression of the lipid peroxidation end product 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) and the level of cleaved caspase-3. In addition, Nrf2 silencing reversed the effects of ORM1 on DOX-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes. In conclusion, ORM1 inhibited DOX-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes by regulating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, which might provide a new treatment strategy for DOX-induced cardiotoxicity.
Copyright © 2020 Xiaoli Cheng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cardamonin protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in mice by restraining oxidative stress and inflammation associated with Nrf2 signaling.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Feb;122:109547. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109547. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31918264
-
Overexpression of Kininogen-1 aggravates oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in DOX-induced cardiotoxicity.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Apr 23;550:142-150. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.02.104. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 33706097
-
Carnosic acid protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through enhancing the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.Food Funct. 2023 Apr 24;14(8):3849-3862. doi: 10.1039/d2fo03904d. Food Funct. 2023. PMID: 37013966
-
MicroRNAs target the PI3K/Akt/p53 and the Sirt1/Nrf2 signaling pathways in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2023 Feb;37(2):e23261. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23261. Epub 2022 Nov 23. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36416353 Review.
-
Role of M6a Methylation in Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024 Sep;24(9):918-928. doi: 10.1007/s12012-024-09898-7. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39026038 Review.
Cited by
-
Sex-related differences in delayed doxorubicin-induced cardiac dysfunction in C57BL/6 mice.Arch Toxicol. 2024 Apr;98(4):1191-1208. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03678-y. Epub 2024 Jan 20. Arch Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38244039
-
Corrigendum to "Orosomucoid 1 Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Cardiomyocytes via Nrf2 Signaling".Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jul 4;2022:9828942. doi: 10.1155/2022/9828942. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35832841 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Modification Status of Human Serum Albumin Caused by Chronic Low-Dose Radiation Exposure in Mamuju, Sulawesi, Indonesia.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Dec 1;11(12):2384. doi: 10.3390/antiox11122384. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36552593 Free PMC article.
-
CD47 antibody protects mice from doxorubicin-induced myocardial damage by suppressing cardiomyocyte apoptosis.Exp Ther Med. 2022 May;23(5):350. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11277. Epub 2022 Mar 24. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35493436 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac Protective Effect of Kirenol against Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy in H9c2 Cells through Nrf2 Signaling via PI3K/AKT Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 23;22(6):3269. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063269. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33806909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Todorova V. K., Makhoul I., Wei J., Klimberg V. S. Circulating miRNA profiles of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients. Annals of Clinical and Laboratory Science. 2017;47(2):115–119. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

