Transcriptome network data in larval zebrafish (Danio rerio) following exposure to the phenylpyrazole fipronil
- PMID: 33134444
- PMCID: PMC7586098
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2020.106413
Transcriptome network data in larval zebrafish (Danio rerio) following exposure to the phenylpyrazole fipronil
Abstract
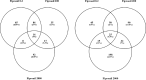
Fipronil is a phenylpyrazole pesticide that is used in both residential and agricultural applications. Fipronil is detected in run-off and water systems that are near areas in which the pesticide has been applied. The pesticide acts to antagonize gamma aminobutyric acid receptors, leading to over-excitation in the central nervous system. Fipronil has relatively high toxicity to fish, but the mechanisms underlying the toxicity are not well understood in embryonic stages. Zebrafish embryos were exposed to a single concentration of fipronil for 48 h at ∼3-4 h-post-fertilization. Following a 7-day depuration phase, transcriptome and behavioral analyses were conducted. Transcriptomics identified neural processes as those differentially expressed with different doses of fipronil (0.2 µg, 200 µg and 2 mg fipronil/L). Gene networks associated with astrocyte differentiation, myelination, neural tube development, brain stem response, innervation, nerve regeneration, astrocyte differentiation, among other pathways were altered with exposure. In addition, miRNA-related events are disrupted by fipronil exposure and genes associated with primary or pri-miRNA processing were increased in larval fish exposed to the pesticide. These data present putative mechanisms associated with neurological impacts at later ages of zebrafish. This is important because it is not clear how early exposure to pesticides like fipronil affect central nervous system function and organisms later in life.
Keywords: Agrochemical; Environmental toxicology; Gene network; Neurotoxicity; Pesticide.
© 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships which have or could be perceived to have influenced the work reported in this article.
Figures
References
-
- Eadie A., Vásquez IC, Liang X, Wang X, Souders CL, II, El Chehouri J, Hoskot R, Feswick A, Cowie AM, Loughery JR, Martyniuk CJ. Residual molecular and behavioral impacts of the phenylpyrazole pesticide fipronil in larval zebrafish (Danio rerio) following embryonic exposure. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D: Genom. Proteom. In press. 2020 - PubMed
-
- Oliveros, JC. (2007-2015) Venny. An interactive tool for comparing lists with Venn's diagrams. https://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/index.html
-
- Cowie A.M., Sarty K.I., Mercer A., Koh J., Kidd K.A, Martyniuk C.J. Molecular networks related to the immune system and mitochondria are targets for the pesticide dieldrin in the zebrafish (Danio rerio) central nervous system. J. Proteom. 2017;157:71–82. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

