Kynurenine pathway in Parkinson's disease-An update
- PMID: 33134567
- PMCID: PMC7585940
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ensci.2020.100270
Kynurenine pathway in Parkinson's disease-An update
Abstract
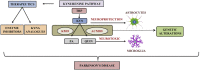
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a complex multi-factorial neurodegenerative disorder where various altered metabolic pathways contribute to the progression of the disease. Tryptophan (TRP) is a major precursor in kynurenine pathway (KP) and it has been discussed in various in vitro studies that the metabolites quinolinic acid (QUIN) causes neurotoxicity and kynurenic acid (KYNA) acts as neuroprotectant respectively. More studies are also focused on the effects of other KP metabolites and its enzymes as it has an association with ageing and PD pathogenesis. Until now, very few studies have targeted the role of genetic mutations in abnormal KP metabolism in adverse conditions of PD. Therefore, the present review gives an updated research studies on KP in connection with PD. Moreover, the review emphasizes on the urge for the development of biomarkers and also this would be an initiative in generating an alternative therapeutic approach for PD.
Keywords: 3-HAA, 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid; 3-HK, 3-hydroxykynurenine; 6-OHDA, 6-hydroxydopamine; AA, anthranilic acid; ACMSD, amino-carboxymuconatesemialdehyde decarboxylase; AD, Alzheimer's disease; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; Ageing; AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; Biomarkers; CNS, central nervous system; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; DA, dopaminergic; FAM, formamidase; IDO-1, indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenases; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; KATs, kynurenine aminotransferases; KMO, kynurenine −3-monooxygenase; KP, Kynurenine pathway; KYN, kynurenine; KYNA, kynurenic acid; Kynurenine pathway (KP); L-DOPA, L-dopamine; LID, L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia; MPTP, 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine; NAD+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NFK, N′-formylkynurenine; NMDA, N-methyl-d-aspartate; PA, picolinic acid; PD, Parkinson's disease; Parkinson's disease (PD); QUIN, quinolinic acid; RBCs, red blood cells; SNpc, substantianigra pars compacta; TDO, tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase; TRP, tryptophan; Therapeutics; XA, xanthurenic acid; ZNS, zonisamide; α-synuclein, αSyn.
© 2020 Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kaavya J., Mahalaxmi I., Dhivya V., Venkatesh B., Arul N., Devi S.M., Cho S.G., Balachandar V. Unraveling correlative roles of dopamine transporter (DAT) and parkin in Parkinson’s disease (PD)-a road to discovery? Brain Res. Bull. 2020;157:169–179. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.02.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dhivya V., Ramkumar S., Illakiyapavai D., Sangeetha M., Ganesan S., Devi S.M., Sasikala K., Balachandar V. Screening of genetic mutations in early onset parkinsonism patients: a family based study in Tamil Nadu population. Int. J. Hum. Genet. 2016;16:158–165. doi: 10.1080/09723757.2016.11886293. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous