Investigation of noradrenergic receptor system in anti-nociception using formalin test in the naked mole rat (Heterocephalus glaber)
- PMID: 33134574
- PMCID: PMC7586093
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05216
Investigation of noradrenergic receptor system in anti-nociception using formalin test in the naked mole rat (Heterocephalus glaber)
Abstract
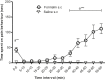
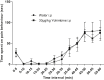
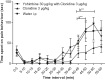
The naked mole rat (NMR) is a rodent that has gained importance as a biomedical research model for various conditions like hypoxic brain injury, cancer and nociception. This study was designed to investigate possible involvement of the noadrenergic receptor system in antinoception in the NMR, using the alpha-2 adrenergic receptor specific ligands clonidine (agonist) and yohimbine (antagonist) in the formalin test. Formalin test followed 30 min after intraperitoneal administration of ligands or control. A total of 96 naked mole rats were used. A significant reduction in nociceptive behaviours was demonstrated after administration of clonidine in the doses 1,3,10 and 30 μg/kg (n = 8 per group). Doses of clonidine above 30 μg/kg caused loss of motor and proprietion skills exhibited by prostration and failure to turn over when placed on their backs. The antinociception by 3 μg/kg clonidine was reversed by administration of 30 μg/kg of yohimbine. The present study demonstrates that the noradrenergic receptor system is present and involved in formalin test-related antinociceptive mechanisms in the NMR, similar to other mammals. Given the increasing importance of the NMR as a model for pain and nociception, the species may prove useful as an animal model for noradrenergic mechanisms in pain modulation.
Keywords: Animal behavior; Animal science; Cell biology; Clonidine; Formalin test; Naked mole rats; Neuroscience; Nociception; Noradrenergic; Pharmaceutical science; Statistics; Yohimbine.
© 2020 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effects of clonidine and yohimbine in the tail flick and hot plate tests in the naked mole rat (Heterocephalus glaber).BMC Res Notes. 2021 May 17;14(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s13104-021-05607-7. BMC Res Notes. 2021. PMID: 34001271 Free PMC article.
-
Intrathecal administration of clonidine or yohimbine decreases the nociceptive behavior caused by formalin injection in the marsh terrapin (Pelomedusa subrufa).Brain Behav. 2014;4(6):850-7. doi: 10.1002/brb3.287. Epub 2014 Oct 2. Brain Behav. 2014. PMID: 25365809 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the presence and antinociceptive function of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in the African naked mole-rat (Heterocephalus glaber).J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2016 Jan;202(1):7-15. doi: 10.1007/s00359-015-1048-x. Epub 2015 Oct 31. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26520141 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of oxotremorine, epibatidine, atropine, mecamylamine and naloxone in the tail-flick, hot-plate, and formalin tests in the naked mole-rat (Heterocephalus glaber).In Vivo. 2014 Jan-Feb;28(1):39-48. In Vivo. 2014. PMID: 24425834
-
Metabolic regulatory clues from the naked mole rat: toward brain regulatory functions during stroke.Brain Res Bull. 2013 Sep;98:44-52. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2013.07.008. Epub 2013 Jul 23. Brain Res Bull. 2013. PMID: 23886571 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of dexamethasone and acetylsalicylic acid on inflammation caused by Complete Freund's adjuvant in the naked mole rat (Heterocephalus glaber).Heliyon. 2022 Feb 8;8(2):e08920. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e08920. eCollection 2022 Feb. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 35198780 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of clonidine and yohimbine in the tail flick and hot plate tests in the naked mole rat (Heterocephalus glaber).BMC Res Notes. 2021 May 17;14(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s13104-021-05607-7. BMC Res Notes. 2021. PMID: 34001271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abelson K.S.P., Höglund A.U. The effects of the α2-adrenergic receptor agonists clonidine and rilmenidine, and antagonists yohimbine and efaroxan, on the spinal cholinergic receptor system in the rat. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2004;94:153–160. - PubMed
-
- Abelson K.S.P., Roughan J.V. Animal models in pain research. In: Hau J., Schapiro S.J., editors. Handbook of Laboratory Animal Science, Volume II, Third Edition: Animal Models. C R C Press LLC; Boca Raton: 2011. pp. 123–147. Chapter 7.
-
- Abiyselassie G.A. Overview of African naked mole-rat (Heterocephalus glaber) for bioprospecting and access and benefit sharing in Ethiopia. GSC Biol. Pharm. Sci. 2018;4(1):25–37.
-
- Ajao F., Afolabi A.O., Udoh U., Azeez O. The formalin test in African toad (Bufo regularis) - a novel pain model in Amphibians. Afr. J. Biomed. Res. 2007;8:123–125.
-
- Alfa K., Antagonistlerinin K., Ruminantlarda D., Ãœzerine Z., Shah D., Mingxing M., Hu-Li A review on the current use of alpha-2 agonists in small ruminants. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fakult. Derg. 2014;20
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

