Robust and Specific Secretory IgA Against SARS-CoV-2 Detected in Human Milk
- PMID: 33134887
- PMCID: PMC7586930
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101735
Robust and Specific Secretory IgA Against SARS-CoV-2 Detected in Human Milk
Abstract
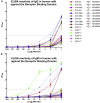
The SARS-CoV-2 immune response in human milk has not yet been examined, although protecting infants and young children from COVID-19 is critical for limiting community transmission and preventing serious illness and death. Here, milk samples from eight COVID-19-recovered and seven COVID-19-suspected donors were tested for antibody (Ab) binding to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein. All samples exhibited significant specific IgA reactivity to the full Spike, whereas 80% exhibited significant IgA and secretory (s)Ab binding to the Receptor-Binding Domain (RBD). Additionally, 67% samples exhibited IgG and/or IgM binding to RBD. IgA and sAb titers were highly correlated, indicating most IgA to be sIgA. Overall, these data indicate that a robust sIgA-dominant SARS-CoV-2 Ab response in human milk after infection should be expected in a significant majority of individuals. Further research is highly warranted to determine Ab functionality and the potential for exploiting extracted milk sIgA for therapeutic use.
Keywords: Immunology; Pediatrics; Virology.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Mount Sinai has licensed serological assays to commercial entities and has filed for patent protection for SARS-CoV-2 serological and milk assays.
Figures



References
-
- Ahlstedt S., Carlsson B., Fällström S.P., Hanson L.A., Holmgren J., Lidin-Janson G., Lindblad B.S., Jodal U., Kaijser B., Solh-Akerlund A. Antibodies in human serum and milk induced by enterobacteria and food proteins. Ciba Found. Symp. 1977;1:115–134. - PubMed
-
- Brandtzaeg P. The mucosal immune system and its integration with the mammary glands. J. Pediatr. 2010;156:S8–S15. - PubMed
-
- Centeno-Tablante E., Medina-Rivera M., Finkelstein J.L., Rayco-Solon P., Garcia-Casal M.N., Rogers L., Ghezzi-Kopel K., Ridwan P., Peña-Rosas J.P., Mehta S. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 through breast milk and breastfeeding: a living systematic review. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020 doi: 10.1111/nyas.14477. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

