An Adaptive Control Scheme for Interleukin-2 Therapy
- PMID: 33134893
- PMCID: PMC7588844
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101663
An Adaptive Control Scheme for Interleukin-2 Therapy
Abstract
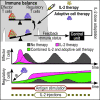
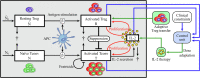
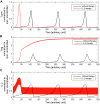
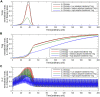
Regulatory T cells (Treg) are suppressor cells that control self-reactive and excessive effector conventional T helper cell (Tconv) responses. Breakdown of the balance between Tregs and Tconvs is a hallmark of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is a growth factor for both populations and subtle leverage to restore the healthy immune balance in IL-2 therapy. By using a mechanistic mathematical model, we introduced an adaptive control strategy to design the minimal therapeutic IL-2 dosage required to increase and stabilize Treg population and restrict inflammatory response. This adaptive protocol allows for dose adjustments based on the feedback of the immune kinetics of the patient. Our simulation results showed that a minimal Treg population was required to restrict the transient side effect of IL-2 injections on the effector Tconv response. In silico results suggested that a combination of IL-2 and adoptive Treg transfer therapies can limit this side effect.
Keywords: Biological Sciences; Immunology; Mathematical Bioscience.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bahremand S., Ko H.S., Balouchzadeh R., Lee H.F., Park S., Kwon G. Neural network-based model predictive control for type 1 diabetic rats on artificial pancreas system. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2019;57:177–191. - PubMed
-
- Fontes F.A., Pereira F.L. Model predictive control of impulsive dynamical systems. IFAC Proc. Volumes. 2012;45:305–310.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

