Increased Callosal Connectivity in Reeler Mice Revealed by Brain-Wide Input Mapping of VIP Neurons in Barrel Cortex
- PMID: 33135045
- PMCID: PMC7869096
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhaa280
Increased Callosal Connectivity in Reeler Mice Revealed by Brain-Wide Input Mapping of VIP Neurons in Barrel Cortex
Abstract
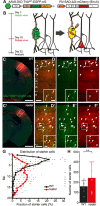
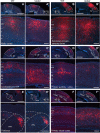
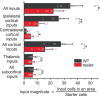
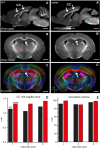
The neocortex is composed of layers. Whether layers constitute an essential framework for the formation of functional circuits is not well understood. We investigated the brain-wide input connectivity of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) expressing neurons in the reeler mouse. This mutant is characterized by a migration deficit of cortical neurons so that no layers are formed. Still, neurons retain their properties and reeler mice show little cognitive impairment. We focused on VIP neurons because they are known to receive strong long-range inputs and have a typical laminar bias toward upper layers. In reeler, these neurons are more dispersed across the cortex. We mapped the brain-wide inputs of VIP neurons in barrel cortex of wild-type and reeler mice with rabies virus tracing. Innervation by subcortical inputs was not altered in reeler, in contrast to the cortical circuitry. Numbers of long-range ipsilateral cortical inputs were reduced in reeler, while contralateral inputs were strongly increased. Reeler mice had more callosal projection neurons. Hence, the corpus callosum was larger in reeler as shown by structural imaging. We argue that, in the absence of cortical layers, circuits with subcortical structures are maintained but cortical neurons establish a different network that largely preserves cognitive functions.
Keywords: VIP neurons; barrel cortex; corpus callosum; rabies tracing; reelin.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permission@oup.com.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Distribution and morphology of callosal commissural neurons within the motor cortex of normal and reeler mice.J Comp Neurol. 1985 Feb 1;232(1):83-98. doi: 10.1002/cne.902320108. J Comp Neurol. 1985. PMID: 3973085
-
Brain-Wide Maps of Synaptic Input to Cortical Interneurons.J Neurosci. 2016 Apr 6;36(14):4000-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3967-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27053207 Free PMC article.
-
Receptive-field properties of transcallosal visual cortical neurons in the normal and reeler mouse.J Neurophysiol. 1983 Oct;50(4):838-48. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.4.838. J Neurophysiol. 1983. PMID: 6313871
-
The Functioning of a Cortex without Layers.Front Neuroanat. 2017 Jul 12;11:54. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2017.00054. eCollection 2017. Front Neuroanat. 2017. PMID: 28747874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Dislocated neurons and neural network: hodological study of the motor cortex of the reeler mutant mouse].Hokkaido Igaku Zasshi. 1991 May;66(3):268-85. Hokkaido Igaku Zasshi. 1991. PMID: 1909294 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
A method to estimate the cellular composition of the mouse brain from heterogeneous datasets.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Dec 21;18(12):e1010739. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010739. eCollection 2022 Dec. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 36542673 Free PMC article.
-
VIP-Expressing GABAergic Neurons: Disinhibitory vs. Inhibitory Motif and Its Role in Communication Across Neocortical Areas.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Feb 10;16:811484. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.811484. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35221922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
VIP-to-SST Cell Circuit Motif Shows Differential Short-Term Plasticity across Sensory Areas of Mouse Cortex.J Neurosci. 2025 Mar 26;45(13):e0949242025. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0949-24.2025. J Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39919833
-
Functional thalamocortical innervation of VIP- and SST-expressing GABAergic interneurons in mouse barrel cortex.iScience. 2025 Apr 28;28(6):112539. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112539. eCollection 2025 Jun 20. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40612908 Free PMC article.
-
The Reelin receptor ApoER2 is a cargo for the adaptor protein complex AP-4: Implications for Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia.Prog Neurobiol. 2024 Mar;234:102575. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2024.102575. Epub 2024 Jan 26. Prog Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38281682 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ährlund-Richter S, Xuan Y, Anna van Lunteren J, Kim H, Ortiz C, Pollak Dorocic I, Meletis K, Carlén M. 2019. A whole-brain atlas of monosynaptic input targeting four different cell types in the medial prefrontal cortex of the mouse. Nat Neurosci. 22:657–668. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

