Neutralization of S100A4 induces stabilization of atherosclerotic plaques: role of smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 33135065
- PMCID: PMC8752361
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa311
Neutralization of S100A4 induces stabilization of atherosclerotic plaques: role of smooth muscle cells
Abstract
Aims: During atherosclerosis, smooth muscle cells (SMCs) accumulate in the intima where they switch from a contractile to a synthetic phenotype. From porcine coronary artery, we isolated spindle-shaped (S) SMCs exhibiting features of the contractile phenotype and rhomboid (R) SMCs typical of the synthetic phenotype. S100A4 was identified as a marker of R-SMCs in vitro and intimal SMCs, in pig and man. S100A4 exhibits intra- and extracellular functions. In this study, we investigated the role of extracellular S100A4 in SMC phenotypic transition.
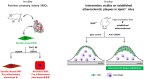
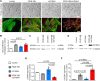
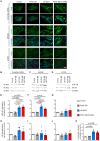
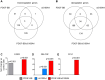
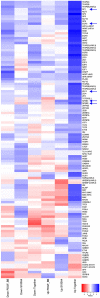
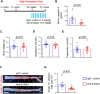
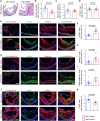
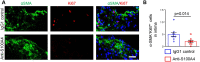
Methods and results: S-SMCs were treated with oligomeric recombinant S100A4 (oS100A4), which induced nuclear factor (NF)-κB activation. Treatment of S-SMCs with oS100A4 in combination with platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-BB induced a complete SMC transition towards a pro-inflammatory R-phenotype associated with NF-κB activation, through toll-like receptor-4. RNA sequencing of cells treated with oS100A4/PDGF-BB revealed a strong up-regulation of pro-inflammatory genes and enrichment of transcription factor binding sites essential for SMC phenotypic transition. In a mouse model of established atherosclerosis, neutralization of extracellular S100A4 decreased area of atherosclerotic lesions, necrotic core, and CD68 expression and increased α-smooth muscle actin and smooth muscle myosin heavy chain expression.
Conclusion: We suggest that the neutralization of extracellular S100A4 promotes the stabilization of atherosclerotic plaques. Extracellular S100A4 could be a new target to influence the evolution of atherosclerotic plaques.
Keywords: ApoE−/−; CD68; Extracellular S100A4; NF-κB; RAGE; Smooth muscle myosin heavy chains; TLR4; α-Smooth muscle actin.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Extracellular role of S100 calcium-binding protein A4 in atherosclerosis.Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Jan 7;118(1):1-3. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab166. Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 33964135 No abstract available.
-
c-Src regulatory role of NOX5 activation and hypertension: a new piece of the puzzle.Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Mar 25;118(5):1170-1172. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab265. Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 34352096 No abstract available.
References
-
- Basatemur GL, Jorgensen HF, Clarke MCH, Bennett MR, Mallat Z. Vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol 2019;16:727–744. - PubMed
-
- Allahverdian S, Chehroudi AC, McManus BM, Abraham T, Francis GA. Contribution of intimal smooth muscle cells to cholesterol accumulation and macrophage-like cells in human atherosclerosis. Circulation 2014;129:1551–1559. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

