A mutation in SLC20A2 (c.C1849T) promotes proliferation while inhibiting hypertrophic differentiation in ATDC5 chondrocytes
- PMID: 33135420
- PMCID: PMC7649514
- DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.911.BJR-2020-0112.R1
A mutation in SLC20A2 (c.C1849T) promotes proliferation while inhibiting hypertrophic differentiation in ATDC5 chondrocytes
Abstract
Aims: This study aimed to investigate the effect of solute carrier family 20 member 2 (SLC20A2) gene mutation (identified from a hereditary multiple exostoses family) on chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation.
Methods: ATDC5 chondrocytes were cultured in insulin-transferrin-selenium medium to induce differentiation. Cells were transfected with pcDNA3.0 plasmids with either a wild-type (WT) or mutated (MUT) SLC20A2 gene. The inorganic phosphate (Pi) concentration in the medium of cells was determined. The expression of markers of chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation, the Indian hedgehog (Ihh), and parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) pathway were evaluated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and western blotting.
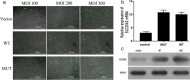
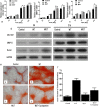
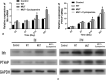
Results: The expression of SLC20A2 in MUT group was similar to WT group. The Pi concentration in the medium of cells in MUT group was significantly higher than WT group, which meant the SLC20A2 mutation inhibited Pi uptake in ATDC5 chondrocytes. The proliferation rate of ATDC5 chondrocytes in MUT group was greater than WT group. The expression of aggrecan (Acan), α-1 chain of type II collagen (COL2A1), and SRY-box transcription factor 9 (SOX9) were higher in MUT group than WT group. However, the expression of Runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2), α-1 chain of type X collagen (COL10A1), and matrix metallopeptidase 13 (MMP13) was significantly decreased in the MUT group. Similar results were obtained by Alcian blue and Alizarin red staining. The expression of Ihh and PTHrP in MUT group was higher than WT group. An inhibitor (cyclopamine) of Ihh/PTHrP signalling pathway inhibited the proliferation and restored the differentiation of chondrocytes in MUT group.
Conclusion: A mutation in SLC20A2 (c.C1948T) decreases Pi uptake in ATDC5 chondrocytes. SLC20A2 mutation promotes chondrocyte proliferation while inhibiting chondrocyte differentiation. The Ihh/PTHrP signalling pathway may play an important role in this process. Cite this article: Bone Joint Res 2020;9(11):751-760.
Keywords: Chondrocyte; Differentiation; Phosphate; Proliferation; SLC20A2.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Suramin enhances chondrogenic properties by regulating the p67phox/PI3K/AKT/SOX9 signalling pathway.Bone Joint Res. 2022 Oct;11(10):723-738. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.1110.BJR-2022-0013.R2. Bone Joint Res. 2022. PMID: 36222195 Free PMC article.
-
Mef2a is a positive regulator of Col10a1 gene expression during chondrocyte maturation.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Jun 15;15(6):4020-4032. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 37434855 Free PMC article.
-
Ddx5 participates in regulation of Col10a1 expression and chondrocyte hypertrophic differentiation in vitro.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Apr 15;16(4):1454-1467. doi: 10.62347/ZDBO3541. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38715834 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of growth factors regulating chondrocyte differentiation in the developing embryo.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001;9 Suppl A:S109-17. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001. PMID: 11680674 Review.
-
PTHrP and skeletal development.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Apr;1068:1-13. doi: 10.1196/annals.1346.002. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. PMID: 16831900 Review.
Cited by
-
Suramin enhances chondrogenic properties by regulating the p67phox/PI3K/AKT/SOX9 signalling pathway.Bone Joint Res. 2022 Oct;11(10):723-738. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.1110.BJR-2022-0013.R2. Bone Joint Res. 2022. PMID: 36222195 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McFarlane J, Knight T, Sinha A, et al. . Exostoses, enchondromatosis and metachondromatosis; diagnosis and management. Acta Orthop Belg. 2016;82(1):102–105. - PubMed
-
- Wuyts W, Radersma R, Storm K, Vits L. An optimized DHPLC protocol for molecular testing of the EXT1 and EXT2 genes in hereditary multiple osteochondromas. Clin Genet. 2005;68(6):542–547. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

