Effect of material selection on tibial post stresses in posterior-stabilized knee prosthesis
- PMID: 33135462
- PMCID: PMC7649505
- DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.911.BJR-2020-0019.R2
Effect of material selection on tibial post stresses in posterior-stabilized knee prosthesis
Abstract
Aims: The material and design of knee components can have a considerable effect on the contact characteristics of the tibial post. This study aimed to analyze the stress distribution on the tibial post when using different grades of polyethylene for the tibial inserts. In addition, the contact properties of fixed-bearing and mobile-bearing inserts were evaluated.
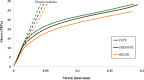
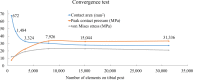
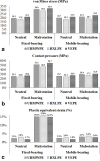
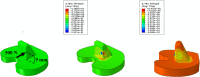
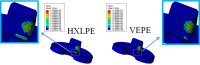
Methods: Three different grades of polyethylene were compared in this study; conventional ultra high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), highly cross-linked polyethylene (HXLPE), and vitamin E-stabilized polyethylene (VEPE). In addition, tibial baseplates with a fixed-bearing and a mobile-bearing insert were evaluated to understand differences in the contact properties. The inserts were implanted in neutral alignment and with a 10° internal malrotation. The contact stress, von Mises stress, and equivalent plastic strain (PEEQ) on the tibial posts were extracted for comparison.
Results: The stress and strain on the tibial post for the three polyethylenes greatly increased when the insert was placed in malrotation, showing a 38% to 56% increase in von Mises stress and a 335% to 434% increase in PEEQ. The VEPE insert had the lowest PEEQ among the three materials. The mobile-bearing design exhibited a lower increase in stress and strain around the tibial posts than the fixed-bearing design.
Conclusion: Using VEPE for the tibial component potentially eliminates the risk of material permanent deformation. The mobile-bearing insert can help to avoid a dramatic increase in plastic strain around the tibial post in cases of malrotation. The mobility allows the pressure to be distributed on the tibial post and demonstrated lower stresses with all three polyethylenes simulated. Cite this article: Bone Joint Res 2020;9(11):768-777.
Keywords: Highly cross-linked; Malposition; Polyethylene; Stress-strain distribution; Vitamin E-stabilized.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Wear of contemporary total knee replacements--a knee simulator study of six current designs.Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2009 Aug;24(7):583-8. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2009.04.007. Epub 2009 May 17. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2009. PMID: 19450910
-
The effect of malalignment on stresses in polyethylene component of total knee prostheses--a finite element analysis.Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2002 Feb;17(2):140-6. doi: 10.1016/s0268-0033(01)00109-7. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2002. PMID: 11832264
-
Mobile-bearing insert translational and rotational kinematics in a PCL-retaining total knee arthroplasty.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2009 Jun;95(4):254-9. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2009.03.012. Epub 2009 May 12. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2009. PMID: 19442597
-
Crosslink Density Is Reduced and Oxidation Is Increased in Retrieved Highly Crosslinked Polyethylene TKA Tibial Inserts.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017 Jan;475(1):128-136. doi: 10.1007/s11999-016-4820-5. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017. PMID: 27084716 Free PMC article.
-
Mobile-bearing knee systems: ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene wear and design issues.Instr Course Lect. 2005;54:195-205. Instr Course Lect. 2005. PMID: 15948447 Review.
Cited by
-
Different tibial rotational axes can be applied in combination according to the tibial tuberosity-posterior cruciate ligament distance in total knee arthroplasty.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022 Oct 10;23(1):906. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05859-9. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022. PMID: 36217137 Free PMC article.
-
[Accuracy of patellar tendon at the attachment as anatomic landmark for rotational alignment of tibial component].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Jun 15;36(6):722-728. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202202040. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35712930 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Gender differences affect the location of the patellar tendon attachment site for tibial rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty.J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 Jul 26;17(1):362. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03248-5. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 35883141 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arikupurathu OM, Johnston L, MacInnes A, Nicol G, Nassif M. Medium- to long-term results of the Nexgen legacy posterior stabilized Fixed-Bearing knee replacement. J Knee Surg. 2019;32(6):554–559. - PubMed
-
- García-Crespo R, Marco F, Moro LE, et al. . Midterm results of Optetrak posterior-stabilized total knee system after 7 to 12 years in a university hospital. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(8):1326–1331. - PubMed
-
- Ulivi M, Orlandini L, Meroni V, Consonni O, Sansone V. Survivorship at minimum 10-year follow-up of a rotating-platform, mobile-bearing, posterior-stabilised total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(6):1669–1675. - PubMed
-
- Insall JN, Lachiewicz PF, Burstein AH. The posterior stabilized condylar prosthesis: a modification of the total condylar design. two to four-year clinical experience. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982;64-A(9):1317–1323. - PubMed
-
- Huang C-H, Liau J-J, Huang C-H, Cheng C-K. Influence of post-cam design on stresses on posterior-stabilized tibial posts. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;450:150–156. - PubMed

