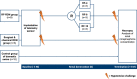
A drug-induced hypotensive challenge to verify catheter-based radiofrequency renal denervation in an obese hypertensive swine model
- PMID: 33136224
- PMCID: PMC9151536
- DOI: 10.1007/s00392-020-01764-0
A drug-induced hypotensive challenge to verify catheter-based radiofrequency renal denervation in an obese hypertensive swine model
Abstract
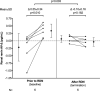
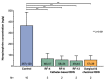
Objective: Sham-controlled trials provided proof-of-principle for the blood pressure-lowering effect of catheter-based renal denervation (RDN). However, indicators for the immediate assessment of treatment success are lacking. This study sought to investigate the impact of RDN on renal renin arteriovenous difference (renal renin AV-Δ) following a hypotensive challenge (HC).
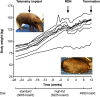
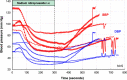
Methods: Twelve hypertensive Ossabaw swine underwent either combined surgical and chemical (n = 3) or catheter-based RDN (n = 9). A telemetry monitor was implanted to acquire hemodynamic data continuously. Before and after RDN, a sodium nitroprusside-induced HC was performed. Renal renin AV-Δ was calculated as the difference of plasma renin concentrations drawn from the renal artery and vein.
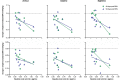
Results: In total, complete renal renin AV data were obtained in eight animals at baseline and six animals at baseline and 3 months of follow-up. Baseline renal renin AV-Δ correlated inversely with change in 24-h minimum systolic (- 0.764, p = 0.02), diastolic (r = - 0.679, p = 0.04), and mean (r = - 0.663, p = 0.05) blood pressure. In the animals with complete renin secretion data at baseline and follow-up, the HC increased renal renin AV-Δ at baseline, while this effect was attenuated following RDN (0.55 ± 0.34 pg/ml versus - 0.10 ± 0.16 pg/ml, p = 0.003). Renin urinary excretion remained unchanged throughout the study (baseline 0.286 ± 0.187 pg/ml versus termination 0.305 ± 0.072 pg/ml, p = 0.789).
Conclusion: Renin secretion induced by HC was attenuated following RDN and may serve as an indicator for patient selection and guide successful RDN procedures.
Keywords: Arterial hypertension; Hypotensive challenge; Renal arterial microanatomy; Renal denervation.
© 2020. The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pulmonary and Systemic Hemodynamics following Multielectrode Radiofrequency Catheter Renal Denervation in Acutely Induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Swine.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Nov 2;2021:4248111. doi: 10.1155/2021/4248111. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34765677 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of renal sympathetic denervation using saline-irrigated radiofrequency ablation catheter on the activity of the renin-angiotensin system and endothelin-1.J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2014 Dec;15(4):532-9. doi: 10.1177/1470320313506480. Epub 2014 Feb 4. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2014. PMID: 24496516
-
Catheter-based radio-frequency renal nerve denervation lowers blood pressure in obese hypertensive swine model.J Hypertens. 2016 Sep;34(9):1854-62. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001021. J Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 27379536
-
Renal Denervation for Treating Hypertension: Current Scientific and Clinical Evidence.JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019 Jun 24;12(12):1095-1105. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2019.02.050. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019. PMID: 31221299 Review.
-
Catheter-based renal denervation as adjunct to pulmonary vein isolation for treatment of atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Hypertens. 2020 May;38(5):783-790. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000002335. J Hypertens. 2020. PMID: 32238783
Cited by
-
Off-the-shelf barrier for emergency intubation in the cardiac catheterization laboratory during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.Clin Res Cardiol. 2020 Dec;109(12):1507-1509. doi: 10.1007/s00392-020-01696-9. Epub 2020 Jul 4. Clin Res Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32623491 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying very low-risk STEMI patients for early ICU discharge in the COVID-19 era.Clin Res Cardiol. 2020 Dec;109(12):1582-1584. doi: 10.1007/s00392-020-01702-0. Epub 2020 Jul 13. Clin Res Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32661674 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Impact of COVID-19 outbreak on regional STEMI care in Germany.Clin Res Cardiol. 2020 Dec;109(12):1511-1521. doi: 10.1007/s00392-020-01703-z. Epub 2020 Jul 16. Clin Res Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32676681 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal trends in the presentation of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular emergencies during the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany: an analysis of health insurance claims.Clin Res Cardiol. 2020 Dec;109(12):1540-1548. doi: 10.1007/s00392-020-01723-9. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Clin Res Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32749558 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kandzari DE, Böhm M, Mahfoud F, et al. Effect of renal denervation on blood pressure in the presence of antihypertensive drugs: 6-month efficacy and safety results from the SPYRAL HTN-ON MED proof-of-concept randomised trial. Lancet. 2018;391:2346–2355. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30951-6. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

