Statistical Learning and Language Impairments: Toward More Precise Theoretical Accounts
- PMID: 33136519
- PMCID: PMC7961654
- DOI: 10.1177/1745691620953082
Statistical Learning and Language Impairments: Toward More Precise Theoretical Accounts
Abstract
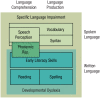
Statistical-learning (SL) theory offers an experience-based account of typical and atypical spoken and written language acquisition. Recent work has provided initial support for this view, tying individual differences in SL abilities to linguistic skills, including language impairments. In the current article, we provide a critical review of studies testing SL abilities in participants with and without developmental dyslexia and specific language impairment and discuss the directions that this field of research has taken so far. We identify substantial vagueness in the demarcation lines between different theoretical constructs (e.g., "statistical learning," "implicit learning," and "procedural learning") as well as in the mappings between experimental tasks and these theoretical constructs. Moreover, we argue that current studies are not designed to contrast different theoretical approaches but rather test singular confirmatory predictions without including control tasks showing normal performance. We end by providing concrete suggestions for how to advance research on SL deficits in language impairments.
Keywords: developmental disorders; dyslexia; implicit learning; language acquisition; literacy; procedural learning; reading; specific language impairment; statistical learning.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Adriaans F., Kager R. (2010). Adding generalization to statistical learning: The induction of phonotactics from continuous speech. Journal of Memory and Language, 62, 311–331. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2009.11.007 - DOI
-
- Altmann G. T. M., Dienes Z., Goode A. (1995). Modality independence of implicitly learned grammatical knowledge. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 21, 899–912. doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.21.4.899 - DOI
-
- American Psychiatric Association. (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed., text rev.). Washington, DC: Author.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

