Opposing functions of Fng1 and the Rpd3 HDAC complex in H4 acetylation in Fusarium graminearum
- PMID: 33137093
- PMCID: PMC7660929
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009185
Opposing functions of Fng1 and the Rpd3 HDAC complex in H4 acetylation in Fusarium graminearum
Abstract
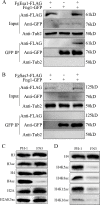
Histone acetylation, balanced by histone acetyltransferase (HAT) and histone deacetylase (HDAC) complexes, affects dynamic transitions of chromatin structure to regulate transcriptional accessibility. However, little is known about the interplay between HAT and HDAC complexes in Fusarium graminearum, a causal agent of Fusarium Head Blight (FHB) that uniquely contains chromosomal regions enriched for house-keeping or infection-related genes. In this study, we identified the ortholog of the human inhibitor of growth (ING1) gene in F. graminearum (FNG1) and found that it specifically interacts with the FgEsa1 HAT of the NuA4 complex. Deletion of FNG1 led to severe growth defects and blocked conidiation, sexual reproduction, DON production, and plant infection. The fng1 mutant was normal in H3 acetylation but significantly reduced in H4 acetylation. A total of 34 spontaneous suppressors of fng1 with faster growth rate were isolated. Most of them were still defective in sexual reproduction and plant infection. Thirty two of them had mutations in orthologs of yeast RPD3, SIN3, and SDS3, three key components of the yeast Rpd3L HDAC complex. Four mutations in these three genes were verified to suppress the defects of fng1 mutant in growth and H4 acetylation. The rest two suppressor strains had a frameshift or nonsense mutation in a glutamine-rich hypothetical protein that may be a novel component of the FgRpd3 HDAC complex in filamentous fungi. FgRpd3, like Fng1, localized in euchromatin. Deletion of FgRPD3 resulted in severe growth defects and elevated H4 acetylation. In contract, the Fgsds3 deletion mutant had only a minor reduction in growth rate but FgSIN3 appeared to be an essential gene. RNA-seq analysis revealed that 48.1% and 54.2% of the genes with altered expression levels in the fng1 mutant were recovered to normal expression levels in two suppressor strains with mutations in FgRPD3 and FgSDS3, respectively. Taken together, our data showed that Fng1 is important for H4 acetylation as a component of the NuA4 complex and functionally related to the FgRpd3 HDAC complex for transcriptional regulation of genes important for growth, conidiation, sexual reproduction, and plant infection in F. graminearum.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures








Similar articles
-
The ING protein Fng2 associated with RPD3 HDAC complex for the regulation of fungal development and pathogenesis in wheat head blight fungus.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 May;268(Pt 2):131938. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131938. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38692539
-
The Fng3 ING protein regulates H3 acetylation and H4 deacetylation by interacting with two distinct histone-modifying complexes.New Phytol. 2022 Sep;235(6):2350-2364. doi: 10.1111/nph.18294. Epub 2022 Jun 21. New Phytol. 2022. PMID: 35653584
-
The HDF1 histone deacetylase gene is important for conidiation, sexual reproduction, and pathogenesis in Fusarium graminearum.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2011 Apr;24(4):487-96. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-10-10-0233. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2011. PMID: 21138346
-
Fng1 is involved in crosstalk between histone acetylation and methylation.Curr Genet. 2021 Aug;67(4):535-538. doi: 10.1007/s00294-021-01167-2. Epub 2021 Feb 28. Curr Genet. 2021. PMID: 33641041 Review.
-
Regulation of Histone Acetylation Modification on Biosynthesis of Secondary Metabolites in Fungi.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 24;26(1):25. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010025. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39795886 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of TRI5 expression and deoxynivalenol biosynthesis by a long non-coding RNA in Fusarium graminearum.Nat Commun. 2024 Feb 9;15(1):1216. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45502-w. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38332031 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Roles of Histone Modifications in Filamentous Fungal Pathogens.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 May 25;8(6):565. doi: 10.3390/jof8060565. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35736048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FgCsn12 Is Involved in the Regulation of Ascosporogenesis in the Wheat Scab Fungus Fusarium graminearum.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 9;23(18):10445. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810445. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142356 Free PMC article.
-
The Histone Deacetylases MoRpd3 and MoHst4 Regulate Growth, Conidiation, and Pathogenicity in the Rice Blast Fungus Magnaporthe oryzae.mSphere. 2021 Jun 30;6(3):101128msphere0011821. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00118-21. Epub 2021 Jun 30. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 34190584 Free PMC article.
-
UvHOS3-mediated histone deacetylation is essential for virulence and negatively regulates ustilaginoidin biosynthesis in Ustilaginoidea virens.Mol Plant Pathol. 2024 Feb;25(2):e13429. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13429. Mol Plant Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38353606 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

