Detection of SARS-CoV-2 from raw patient samples by coupled high temperature reverse transcription and amplification
- PMID: 33137168
- PMCID: PMC7605687
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241740
Detection of SARS-CoV-2 from raw patient samples by coupled high temperature reverse transcription and amplification
Abstract
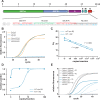
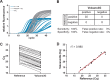
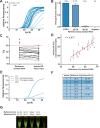
SARS-CoV-2 is spreading globally with unprecedented consequences for modern societies. The early detection of infected individuals is a pre-requisite to contain the virus. Currently, purification of RNA from patient samples followed by RT-PCR is the gold standard to assess the presence of this single-strand RNA virus. However, these procedures are time consuming, require continuous supply of specialized reagents, and are prohibitively expensive in resource-poor settings. Here, we report an improved nucleic-acid-based approach to detect SARS-CoV-2 with the ability to detect as little as five viral genome equivalents. The approach delivers results without the need to purify RNA, reduces handling steps, minimizes costs, and allows evaluation by non-specialized equipment. The use of unprocessed swap samples is enabled by employing a heat-stable RNA- and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase, which performs the double task of stringent reverse transcription of RNA at elevated temperatures as well as PCR amplification of a SARS-CoV-2 specific target gene. As results are obtained within 2 hours and can be read-out by a hand-held LED-screen, this novel protocol will be of particular importance for large-scale virus surveillance in economically constrained settings.
Conflict of interest statement
RK and AM are founders of myPOLS Biotec GmbH, manufacturer of Volcano3G polymerase used in this manuscript. AM is a shareholder of and RK is employed by myPOLS Biotec GmbH. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials. All other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SARS-CoV-2 detection by direct rRT-PCR without RNA extraction.J Clin Virol. 2020 Jul;128:104423. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104423. Epub 2020 May 7. J Clin Virol. 2020. PMID: 32416598 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of Ribonucleic Acid Extraction for Real-Time Reverse Transcription-PCR (rRT-PCR) of SARS-CoV-2: Importance of Internal Control Monitoring.Ann Lab Med. 2020 Nov;40(6):490-492. doi: 10.3343/alm.2020.40.6.490. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Ann Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 32539306 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A Rapid, Simple, Inexpensive, and Mobile Colorimetric Assay COVID-19-LAMP for Mass On-Site Screening of COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 29;21(15):5380. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155380. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32751106 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 by Low Volume Real-Time Single Tube Reverse Transcription Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Using an Exo Probe with an Internally Linked Quencher (Exo-IQ).Clin Chem. 2020 Aug 1;66(8):1047-1054. doi: 10.1093/clinchem/hvaa116. Clin Chem. 2020. PMID: 32384153 Free PMC article.
-
Laboratory diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 - A review of current methods.J Infect Public Health. 2020 Jul;13(7):901-905. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2020.06.005. Epub 2020 Jun 7. J Infect Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32534946 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Engineering of novel DNA polymerase variants for single enzyme quantitative multiplex reverse transcription-PCR.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 18;15(1):26147. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-10211-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40681628 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid visual detection of SARS-CoV-2 by colorimetric loop-mediated isothermal amplification.Biotechniques. 2021 Apr;70(4):218-225. doi: 10.2144/btn-2020-0159. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Biotechniques. 2021. PMID: 33820475 Free PMC article.
-
Suitcase Lab for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Based on Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay.Anal Chem. 2021 Feb 2;93(4):2627-2634. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c04779. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Anal Chem. 2021. PMID: 33471510 Free PMC article.
-
Laboratory-based molecular test alternatives to RT-PCR for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 14;10(10):CD015618. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015618. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39400904
-
An international, interlaboratory ring trial confirms the feasibility of an extraction-less "direct" RT-qPCR method for reliable detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in clinical samples.PLoS One. 2022 Jan 13;17(1):e0261853. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261853. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35025926 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

