EOS789, a broad-spectrum inhibitor of phosphate transport, is safe with an indication of efficacy in a phase 1b randomized crossover trial in hemodialysis patients
- PMID: 33137340
- PMCID: PMC8076057
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.09.035
EOS789, a broad-spectrum inhibitor of phosphate transport, is safe with an indication of efficacy in a phase 1b randomized crossover trial in hemodialysis patients
Abstract
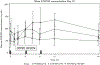
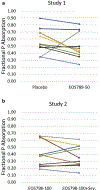
The treatment of hyperphosphatemia remains challenging in patients receiving hemodialysis. This phase 1b study assessed safety and efficacy of EOS789, a novel pan-inhibitor of phosphate transport (NaPi-2b, PiT-1, PiT-2) on intestinal phosphate absorption in patients receiving intermittent hemodialysis therapy. Two cross-over, randomized order studies of identical design (ten patients each) compared daily EOS789 50 mg to placebo with meals and daily EOS789 100 mg vs EOS789 100 mg plus 1600 mg sevelamer with meals. Patients ate a controlled diet of 900 mg phosphate daily for two weeks and began EOS789 on day four. On day ten, a phosphate absorption testing protocol was performed during the intradialytic period. Intestinal fractional phosphate absorption was determined by kinetic modeling of serum data following oral and intravenous doses of 33Phosphate (33P). The results demonstrated no study drug related serious adverse events. Fractional phosphate absorption was 0.53 (95% confidence interval: 0.39,0.67) for placebo vs. 0.49 (0.35,0.63) for 50 mg EOS789; and 0.40 (0.29,0.50) for 100 mg EOS789 vs. 0.36 (0.26,0.47) for 100 mg EOS789 plus 1600 mg sevelamer (all not significantly different). The fractional phosphate absorption trended lower in six patients who completed both studies with EOS789 100 mg compared with placebo. Thus, in this phase 1b study, EOS789 was safe and well tolerated. Importantly, the use of 33P as a sensitive and direct measure of intestinal phosphate absorption allows specific testing of drug efficacy. The effectiveness of EOS789 needs to be evaluated in future phase 2 and phase 3 studies.
Keywords: hemodialysis; intestine; phosphorus absorption; phosphorus radiotracer; sodium-phosphate cotransporters.
Copyright © 2020 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
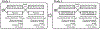


References
-
- Kestenbaum B Mineral metabolism disorders in chronic kidney disease. JAMA. 2011;305:1138–1139. - PubMed
-
- Block GA, Klassen PS, Lazarus JM, et al. Mineral metabolism, mortality, and morbidity in maintenance hemodialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15: 2208–2218. - PubMed
-
- Palmer SC, Hayen A, Macaskill P, et al. Serum levels of phosphorus, parathyroid hormone, and calcium and risks of death and cardiovascular disease in individuals with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2011;305:1119–1127. - PubMed
-
- Chen NX, Moe SM. Pathophysiology of vascular calcification. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2015;13:372–380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

