Bacterial nucleomodulins and cancer: An unresolved enigma
- PMID: 33137543
- PMCID: PMC7644672
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2020.100922
Bacterial nucleomodulins and cancer: An unresolved enigma
Abstract
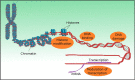
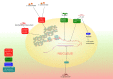
Recent studies in microbial pathogenesis have identified several bacterial proteins with the potential to influence host cell nuclei. This field of research is in its infancy, however it is rapidly growing. In particular, the role of bacterial nucleomodulins in animal oncogenesis is an area that requires attention. Earlier research has suggested the role of nucleomodulins in plant tumor development and these findings may provide us with a better understanding of the role of these proteins in human cancer development. This proposition is further supported by previous identification of nucleomodulins present in bacteria that have been associated with cancer development, but their role in human cancer is unclear. In this article, we provide an update on the status of these nucleomodulins and their role in cancer etiology. We collected information about known bacterial nucleomodulins and tried to relate their mechanistic implication with already known plant tumor development model. The present research indicates that bacterial nucleomodulins may be an important target in cancer etiology and knowledge of their role in human oncogenesis may help us to create suitable alternative cancer management strategies.
Keywords: Host-pathogen interaction; Infection; Oncogenesis; Pathogens; Protein targeting.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest Authors declare no potential conflicts of interest related to text of this manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bacterial nucleomodulins: A coevolutionary adaptation to the eukaryotic command center.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Jan 21;17(1):e1009184. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009184. eCollection 2021 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33476322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial Factors Targeting the Nucleus: The Growing Family of Nucleomodulins.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Mar 31;12(4):220. doi: 10.3390/toxins12040220. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32244550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of potential nucleomodulins of Mycoplasma bovis by direct biotinylation and proximity-based biotinylation approaches.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jul 9;15:1421585. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1421585. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39044956 Free PMC article.
-
When bacteria target the nucleus: the emerging family of nucleomodulins.Cell Microbiol. 2012 May;14(5):622-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2012.01758.x. Epub 2012 Feb 23. Cell Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22289128 Review.
-
Nuclear trafficking of bacterial effector proteins.Cell Microbiol. 2021 Jun;23(6):e13320. doi: 10.1111/cmi.13320. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Cell Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33600054 Review.
Cited by
-
The Identification of a Novel Nucleomodulin MbovP467 of Mycoplasmopsis bovis and Its Potential Contribution in Pathogenesis.Cells. 2024 Mar 29;13(7):604. doi: 10.3390/cells13070604. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38607043 Free PMC article.
-
Campylobacter jejuni regulates cell cycle progression to potentiate host cell invasion.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Jul 16;23(1):343. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02348-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40671100 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiota and cancer: current understanding and mechanistic implications.Clin Transl Oncol. 2022 Feb;24(2):193-202. doi: 10.1007/s12094-021-02690-x. Epub 2021 Aug 13. Clin Transl Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34387847 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arbibe L., Kim D.W., Batsche E., Pedron T., Mateescu B., Muchardt C., Parsot C., Sansonetti P.J. An injected bacterial effector targets chromatin access for transcription factor NF-kappaB to alter transcription of host genes involved in immune responses. Nat. Immunol. 2007;8:47–56. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

