The Impact of a Motor Imagery-Based Training Program on Agility, Speed, and Reaction Time in a Sample of Young Tennis Athletes during Ramadan Fasting: Insights and Implications from a Randomized, Controlled Experimental Trial
- PMID: 33137868
- PMCID: PMC7692860
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12113306
The Impact of a Motor Imagery-Based Training Program on Agility, Speed, and Reaction Time in a Sample of Young Tennis Athletes during Ramadan Fasting: Insights and Implications from a Randomized, Controlled Experimental Trial
Abstract
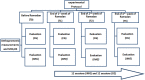
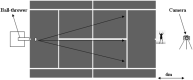
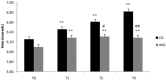
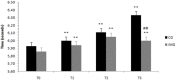
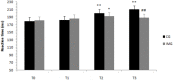
The objective of this study was to explore whether a training program incorporating motor imagery could have an effect on physical performance outcomes in terms of agility, speed, and reaction time in a sample of tennis athletes who fasted during the month of Ramadan. Recruited subjects were 27 young male tennis players, randomly allocated to two groups: the imaging training group (n = 13) and a control group (n = 14). The study was designed as a randomized, controlled experimental study. The control group was engaged in watching videos concerning the history of the Olympic Games, whereas the motor imagery group followed a motor imagery-based training program. Physical performance outcomes were assessed during four sessions (one before Ramadan and three during Ramadan) by means of field tests. Our results revealed a drop in all performance outcomes measured in the middle and at the end of Ramadan for both groups (p < 0.01). The effect of the group × time interaction (p < 0.01) was reported for all physical performance outcomes measured for the two groups. This drop in performance was greater for the control group compared to the motor imagery group in the middle and at the end of Ramadan. This study showed that fasting during Ramadan reduced agility, speed, and reaction time performance for tennis players. A motor imagery-based training program could be an effective approach to reduce the effect of fasting during Ramadan and stabilize physical performance outcomes in terms of agility, speed, and reaction time for male tennis players.
Keywords: Ramadan fasting; agility; motor imagery-based training program; performance; reaction time; speed; sport psychology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

