In Vitro and In Vivo Biological Activity of Berberine Chloride against Uropathogenic E. coli Strains Using Galleria mellonella as a Host Model
- PMID: 33137930
- PMCID: PMC7662377
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25215010
In Vitro and In Vivo Biological Activity of Berberine Chloride against Uropathogenic E. coli Strains Using Galleria mellonella as a Host Model
Abstract
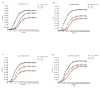
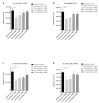
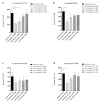
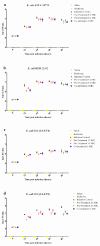
Berberine is an alkaloid of the protoberberine type used in traditional oriental medicine. Its biological activities include documented antibacterial properties against a wide variety of microorganisms; nonetheless, its use against Escherichia coli strains isolated from urinary infections has not yet been widely investigated in vivo. The emergence of antimicrobial resistance requires new therapeutic approaches to ensure the continued effectiveness of antibiotics for the treatment and prevention of urinary infections. Moreover, uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) has developed several virulence factors and resistance to routine antibiotic therapy. To this end, several in vitro and in vivo tests were conducted to assess the activity of berberine on uropathogenic E. coli strains. Galleria mellonella as an infection model was employed to confirm the in vivo translatability of in vitro data on berberine activity and its influence on adhesion and invasion proprieties of E. coli on human bladder cells. In vitro pre-treatment with berberine was able to decrease the adhesive and invasive UPEC ability. In vivo treatment increased the larvae survival infected with UPEC strains and reduced the number of circulating pathogens in larvae hemolymph. These preliminary findings demonstrated the efficacy and reliability of G. mellonella as in vivo model for pre-clinical studies of natural substances.
Keywords: Galleria mellonella; UPEC; antimicrobial activity; berberine chloride; host–pathogen interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNAs regulate innate immunity against uropathogenic and commensal-like Escherichia coli infections in the surrogate insect model Galleria mellonella.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 13;10(1):2570. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59407-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32054914 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrofurantoin Combined With Amikacin: A Promising Alternative Strategy for Combating MDR Uropathogenic Escherichia coli.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Dec 21;10:608547. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.608547. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33409159 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriophage-antibiotic combinations against ciprofloxacin/ceftriaxone-resistant Escherichia coli in vitro and in an experimental Galleria mellonella model.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020 Dec;56(6):106200. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106200. Epub 2020 Oct 17. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020. PMID: 33075514
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of antibiotic resistance patterns, and the correlation between biofilm formation with virulence factors in uropathogenic E. coli isolated from urinary tract infections.Microb Pathog. 2020 Jul;144:104196. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104196. Epub 2020 Apr 10. Microb Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32283258
-
Virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance of uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) isolated from urinary tract infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Aug 4;21(1):753. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06435-7. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34348646 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pharmacokinetics, Tissue Distribution and Excretion of Demethyleneberberine, a Metabolite of Berberine, in Rats and Mice.Molecules. 2023 Nov 23;28(23):7725. doi: 10.3390/molecules28237725. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38067456 Free PMC article.
-
Human breast milk isolated lactic acid bacteria: antimicrobial and immunomodulatory activity on the Galleria mellonella burn wound model.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Sep 6;14:1428525. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1428525. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39310784 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Levels of (p)ppGpp Correlate with Virulence and Biofilm Formation, but Not with Growth, in Strains of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 7;24(4):3315. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043315. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834725 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary Tract Infections Caused by Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Strains-New Strategies for an Old Pathogen.Microorganisms. 2022 Jul 14;10(7):1425. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10071425. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35889146 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary Tract Infections and Associated Factors among Patients with Indwelling Urinary Catheters Attending Bugando Medical Centre a Tertiary Hospital in Northwestern Tanzania.Microorganisms. 2022 Feb 21;10(2):473. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10020473. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35208927 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Muralidharan S., Kumar J.R., Dhanaraj S.A. Estimation of berberine in berberis extracts by RP-HPLC. J. Pharm. Res. 2012;5:2065–2067.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

