Evaluation of Cholinesterase Inhibitory Potential of Different Genotypes of Ziziphus nummularia, Their HPLC-UV, and Molecular Docking Analysis
- PMID: 33137939
- PMCID: PMC7663671
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25215011
Evaluation of Cholinesterase Inhibitory Potential of Different Genotypes of Ziziphus nummularia, Their HPLC-UV, and Molecular Docking Analysis
Abstract
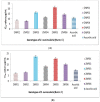
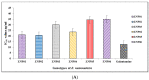
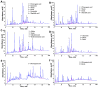
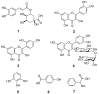
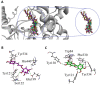
Ziziphus nummularia is an important source of valuable phytoconstituents, which are widely used in traditional medicine system of Indo-Pak sub-continent. In this study we investigated the distribution of phenolic compounds in the fruit pericarps of six different genotypes (ZNP01-06) of Z. nummularia growing in the unexplored hilly areas of Pakistan. The methanolic extracts of these genotypes were screened for total phenolic content (TPC), total flavonoid content (TFC), antioxidant, and cholinesterase inhibitory potentials. The observed biological potentials were explained in terms of the outcome of molecular docking and HPLC analyses. Among them, genotype ZNP02 displayed high TPC (88.50 ± 1.23 μg/mL) and showed potent scavenging activity against DPPH (67.03 ± 1.04 μg/mL) and ABTS (65.3 ± 1.74 μg/mL) in comparison to ascorbic acid (68.7 ± 0.47 μg/mL). Moreover, genotypes ZNP01, ZNP02, and ZNP04 displayed potent inhibition against acetyl and butyryl cholinesterases (AChE and BChE) with IC50 values of 21.2, 20.5, and 23.7 μg/mL (AChE) and 22.7, 24.4, and 33.1 μg/mL (BChE), respectively. Furthermore, the individual compounds in the most potent species ZNP01 responsible for potent enzyme inhibition (identified through HPLC-UV analysis), were computed via docking simulation software to the enzyme structures. Among these compounds rutin exhibited significant binding affinity with value of -9.20 kcal/mol. The differences amongst the phytochemical compositions of the selected genotypes highlighted the genotypic variations in them. Based on our results it was concluded that the selected plant can be used as remedy of oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases. However, further studies are needed to isolate responsible compounds and test the observed potential in vivo, along with toxicological evaluations in animal models.
Keywords: HPLC; Ziziphus nummularia (Burm. f.); characterization; cholinesterase inhibition; genotypes; medicinal uses; molecular docking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
HPLC-DAD finger printing, antioxidant, cholinesterase, and α-glucosidase inhibitory potentials of a novel plant Olax nana.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Jan 3;18(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-2057-9. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 29295712 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of polyphenolic compounds, antioxidant potential, and free amino acids in Ziziphus fruits extract; a study for determining the influence of wider geography.Food Sci Nutr. 2022 Jan 28;10(5):1414-1430. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2726. eCollection 2022 May. Food Sci Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35592302 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical analysis, molecular docking and antiamnesic effects of methanolic extract of Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn seeds in scopolamine induced memory impairment in mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Jan 10;210:198-208. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.08.026. Epub 2017 Aug 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28842342
-
Pharmacological evaluation and in-silico modeling study of compounds isolated from Ziziphus oxyphylla.Heliyon. 2021 Feb 26;7(2):e06367. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06367. eCollection 2021 Feb. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 33681505 Free PMC article.
-
Ziziphus nummularia: A Comprehensive Review of Its Phytochemical Constituents and Pharmacological Properties.Molecules. 2022 Jun 30;27(13):4240. doi: 10.3390/molecules27134240. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35807485 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Flavonoids a Bioactive Compound from Medicinal Plants and Its Therapeutic Applications.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jun 6;2022:5445291. doi: 10.1155/2022/5445291. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35707379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioassay's Directed Isolation-Structure Elucidation and Molecular Docking of Triterpenes from Persea duthiei against Biologically Important Microbial Proteins.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 May 27;2022:3839271. doi: 10.1155/2022/3839271. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35668783 Free PMC article.
-
Notoginsenoside R1-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles targeting the site of injury through inflammatory cells improves heart repair after myocardial infarction.Redox Biol. 2022 Aug;54:102384. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102384. Epub 2022 Jun 24. Redox Biol. 2022. PMID: 35777198 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the potential of Ziziphus nummularia and luteolin-7-O-glucoside as tubulin inhibitors in cancer therapy and survival.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 26;14(1):7202. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57680-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38531974 Free PMC article.
-
Ziziphus mauritiana Lam. Bark and Leaves: Extraction, Phytochemical Composition, In Vitro Bioassays and In Silico Studies.Plants (Basel). 2024 Aug 8;13(16):2195. doi: 10.3390/plants13162195. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204631 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

