Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance by Salmonella enterica Serovar Choleraesuis between Close Domestic and Wild Environments
- PMID: 33137987
- PMCID: PMC7692705
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics9110750
Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance by Salmonella enterica Serovar Choleraesuis between Close Domestic and Wild Environments
Abstract
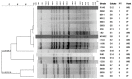
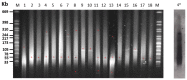
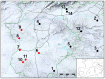
The Salmonellaenterica serovar Choleraesuis affects domestic pig and wild boar (WB), causing clinical salmonellosis. Iberian swine production is based on a free-range production system where WB and Iberian pig (IP) share ecosystems. This study focuses on the negative impact on the pork industry of infections due to this serotype, its role in the spread of antibiotic resistance, and its zoonotic potential. Antibiotic resistance (AR) and genetic relationships were analyzed among 20 strains of S. Choleraesuis isolated from diseased WB and IP sampled in the southwest region of the Iberian Peninsula. AR was studied using the Kirby-Bauer method with the exception of colistin resistance, which was measured using the broth microdilution reference method. Resistance and Class 1 integrase genes were measured using PCR, and the genetic relationship between isolates and plasmid content by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. The results show a higher incidence of AR in isolates from IP. Phylogenetic analysis revealed seven profiles with two groups containing isolates from IP and WB, which indicates circulation of the same clone between species. Most pulsotypes presented with one plasmid of the same size, indicating vertical transmission. AR determinants blaTEM and tetA were routinely found in IP and WB, respectively. One isolate from IP expressed colistin resistance and presented the mcr-1 gene carried by a plasmid. This study suggests that S. Choleraesuis circulates between WB and IP living in proximity, and also that the mobilization of AR genes by plasmids is low. Furthermore, the detection of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance in bacteria from IP is alarming and should be monitored.
Keywords: Iberian pig; Salmonella Choleraesuis; antibiotic resistance; colistin; phylogenetic relationship; plasmid replicon typing; wild boar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Khan M.A., Cao L., Riaz A., Li Y., Jiao Q., Liu Z., Wang H., Meng F., Ma Z. The Harm of Salmonella to Pig Industry and Its Control Measures. Int. J. Appl. Agric. Sci. 2019;5:24.
-
- Gil Molino M., Risco Pérez D., Gonçalves Blanco P., Fernandez Llario P., Quesada Molina A., García Sánchez A., Cuesta Gerveno J.M., Gómez Gordo L., Martín Cano F.E., Pérez Martínez R. Outbreaks of antimicrobial resistant Salmonella Choleraesuis in wild boars piglets from central-western Spain. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2019;66:225–233. doi: 10.1111/tbed.13003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Methner U., Heller M., Bocklisch H. Salmonella enterica subspecies enterica serovar Choleraesuis in a wild boar population in Germany. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2010;56:493–502. doi: 10.1007/s10344-009-0339-3. - DOI
-
- Fedorka-Cray P.J., Gray J.T., Wray C. Salmonella infections in pigs. In: Wray C., Wray A., editors. Salmonella in Domestic Animals. CABI; London, UK: 2000. pp. 191–207.
-
- Asai T., Namimatsu T., Osumi T., Kojima A., Harada K., Aoki H., Sameshima T., Takahashi T. Molecular typing and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella enterica subspecies enterica serovar Choleraesuis isolates from diseased pigs in Japan. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010;33:109–119. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2008.08.004. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

