Use of an Animal Model to Evaluate Anxiolytic Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Tilia tomentosa Moench Bud Extracts
- PMID: 33138077
- PMCID: PMC7693450
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12113328
Use of an Animal Model to Evaluate Anxiolytic Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Tilia tomentosa Moench Bud Extracts
Abstract
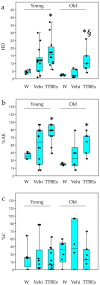
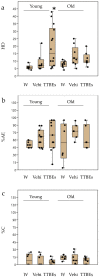
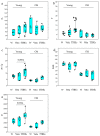
Anxiety disorders are common and complex psychiatric syndromes affecting a broad spectrum of patients. On top of that, we know that aging produces an increase in anxiety vulnerability and sedative consumption. Moreover, stress disorders frequently show a clear gender susceptibility. Currently, the approved pharmacological strategies have severe side effects such as hallucinations, addiction, suicide, insomnia, and loss of motor coordination. Dietary integration with supplements represents an intriguing strategy for improving the efficacy and the safety of synthetic anxiolytics. Accordingly, a recent article demonstrated that glyceric bud extracts from Tilia tomentosa Moench (TTBEs) exert effects that are consistent with anxiolytic activity. However, the effects of these compounds in vivo are unknown. To examine this question, we conducted behavioral analysis in mice. A total of 21 days of oral supplements (vehicle and TTBEs) were assessed by Light Dark and Hole Board tests in male and female mice (young, 3 months; old, 24 months). Interestingly, the principal component analysis revealed gender and age-specific behavioral modulations. Moreover, the diet integration with the botanicals did not modify the body weight gain and the daily intake of water. Our results support the use of TTBEs as dietary supplements for anxiolytic purposes and unveil age and gender-dependent responses.
Keywords: anxiety; bud-derivatives; mice behaviour; mood disorders; nutraceuticals; polyphenols; principal component analysis; supplements.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bud extracts from Tilia tomentosa Moench inhibit hippocampal neuronal firing through GABAA and benzodiazepine receptors activation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Aug 22;172:288-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.06.016. Epub 2015 Jul 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26144285
-
Flavonoids from Tilia americana with anxiolytic activity in plus-maze test.J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Jul 23;118(2):312-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2008.04.019. Epub 2008 Apr 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18539420
-
HPLC/MS analysis and anxiolytic-like effect of quercetin and kaempferol flavonoids from Tilia americana var. mexicana.J Ethnopharmacol. 2010 Jan 8;127(1):91-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2009.09.044. Epub 2009 Sep 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19799990
-
Interactions of a standardized flavonoid fraction from Tilia americana with Serotoninergic drugs in elevated plus maze.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Apr 22;164:319-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.01.029. Epub 2015 Feb 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25656001
-
Formulations of dietary supplements and herbal extracts for relaxation and anxiolytic action: Relarian.Med Sci Monit. 2009 Nov;15(11):RA256-62. Med Sci Monit. 2009. PMID: 19865069 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of Tilia tomentosa Moench Extract on Mouse Small Intestine Neuromuscular Contractility.Nutrients. 2021 Oct 4;13(10):3505. doi: 10.3390/nu13103505. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34684506 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling Niaprazine's Potential: Behavioral Insights into a Re-Emerging Anxiolytic Agent.Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 12;12(9):2087. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12092087. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39335600 Free PMC article.
-
Vitis vinifera L. Pruning Waste for Bud-Preparations as Source of Phenolic Compounds-Traditional and Innovative Extraction Techniques to Produce New Natural Products.Plants (Basel). 2021 Oct 20;10(11):2233. doi: 10.3390/plants10112233. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34834596 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of Tilia americana var. mexicana Against Kainic Acid-induced Damage in Brain, Liver, and Kidney: Behavioral and Biochemical Changes.Iran J Pharm Res. 2022 May 3;21(1):e126914. doi: 10.5812/ijpr-126914. eCollection 2022 Dec. Iran J Pharm Res. 2022. PMID: 36060909 Free PMC article.
-
Anxiety and Metabolic Disorders: The Role of Botanicals.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Jan 28;45(2):1037-1053. doi: 10.3390/cimb45020068. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36826013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pandey M., Verma R.K., Saraf S.A. Nutraceuticals: New era of medicine and health. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2010;3:11–15.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

