The Transcriptional Network in the Arabidopsis Circadian Clock System
- PMID: 33138078
- PMCID: PMC7692566
- DOI: 10.3390/genes11111284
The Transcriptional Network in the Arabidopsis Circadian Clock System
Abstract
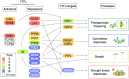
The circadian clock is the biological timekeeping system that governs the approximately 24-h rhythms of genetic, metabolic, physiological and behavioral processes in most organisms. This oscillation allows organisms to anticipate and adapt to day-night changes in the environment. Molecular studies have indicated that a transcription-translation feedback loop (TTFL), consisting of transcriptional repressors and activators, is essential for clock function in Arabidopsis thaliana (Arabidopsis). Omics studies using next-generation sequencers have further revealed that transcription factors in the TTFL directly regulate key genes implicated in clock-output pathways. In this review, the target genes of the Arabidopsis clock-associated transcription factors are summarized. The Arabidopsis clock transcriptional network is partly conserved among angiosperms. In addition, the clock-dependent transcriptional network structure is discussed in the context of plant behaviors for adapting to day-night cycles.
Keywords: arabidopsis; circadian clock; plant development; transcription factors; transcriptional network.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the writing of the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evolutionary Insight into the Clock-Associated PRR5 Transcriptional Network of Flowering Plants.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 27;9(1):2983. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39720-2. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30814643 Free PMC article.
-
Ambient temperature signal feeds into the circadian clock transcriptional circuitry through the EC night-time repressor in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Cell Physiol. 2014 May;55(5):958-76. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcu030. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24500967
-
From a repressilator-based circadian clock mechanism to an external coincidence model responsible for photoperiod and temperature control of plant architecture in Arabodopsis thaliana.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2013;77(1):10-6. doi: 10.1271/bbb.120765. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23291766 Review.
-
A systematic survey in Arabidopsis thaliana of transcription factors that modulate circadian parameters.BMC Genomics. 2008 Apr 21;9:182. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-182. BMC Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18426557 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms at the core of the plant circadian oscillator.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2016 Dec;23(12):1061-1069. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3327. Epub 2016 Dec 6. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27922614 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Circadian Clock Coordinates the Tradeoff between Adaptation to Abiotic Stresses and Yield in Crops.Biology (Basel). 2023 Oct 24;12(11):1364. doi: 10.3390/biology12111364. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37997963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The biology of time: dynamic responses of cell types to developmental, circadian and environmental cues.Plant J. 2022 Feb;109(4):764-778. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15589. Epub 2021 Dec 6. Plant J. 2022. PMID: 34797944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diurnal Rhythms in the Red Seaweed Gracilariopsis chorda are Characterized by Unique Regulatory Networks of Carbon Metabolism.Mol Biol Evol. 2024 Feb 1;41(2):msae012. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msae012. Mol Biol Evol. 2024. PMID: 38267085 Free PMC article.
-
Plant clock modifications for adapting flowering time to local environments.Plant Physiol. 2022 Sep 28;190(2):952-967. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiac107. Plant Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35266545 Free PMC article.
-
Diurnal rhythms in durum wheat triggered by Rhopalosiphum padi (bird cherry-oat aphid).BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Apr 10;25(1):459. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06100-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40211135 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

