XIAP's Profile in Human Cancer
- PMID: 33138314
- PMCID: PMC7692959
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10111493
XIAP's Profile in Human Cancer
Abstract
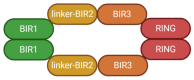
XIAP, the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein, regulates cell death signaling pathways through binding and inhibiting caspases. Mounting experimental research associated with XIAP has shown it to be a master regulator of cell death not only in apoptosis, but also in autophagy and necroptosis. As a vital decider on cell survival, XIAP is involved in the regulation of cancer initiation, promotion and progression. XIAP up-regulation occurs in many human diseases, resulting in a series of undesired effects such as raising the cellular tolerance to genetic lesions, inflammation and cytotoxicity. Hence, anti-tumor drugs targeting XIAP have become an important focus for cancer therapy research. RNA-XIAP interaction is a focus, which has enriched the general profile of XIAP regulation in human cancer. In this review, the basic functions of XIAP, its regulatory role in cancer, anti-XIAP drugs and recent findings about RNA-XIAP interactions are discussed.
Keywords: XIAP; apoptosis; cancer; non-coding RNA; therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
XIAP as a multifaceted molecule in Cellular Signaling.Apoptosis. 2022 Aug;27(7-8):441-453. doi: 10.1007/s10495-022-01734-z. Epub 2022 Jun 4. Apoptosis. 2022. PMID: 35661061 Review.
-
The RING domain in the anti-apoptotic protein XIAP stabilizes c-Myc protein and preserves anchorage-independent growth of bladder cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2019 Apr 12;294(15):5935-5944. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005621. Epub 2019 Feb 28. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30819803 Free PMC article.
-
S-nitrosylation of XIAP at Cys 213 of BIR2 domain impairs XIAP's anti-caspase 3 activity and anti-apoptotic function.Apoptosis. 2015 Apr;20(4):491-9. doi: 10.1007/s10495-015-1087-3. Apoptosis. 2015. PMID: 25578648
-
XIAP inhibition of caspase-3 preserves its association with the Apaf-1 apoptosome and prevents CD95- and Bax-induced apoptosis.Cell Death Differ. 2002 Sep;9(9):881-92. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401069. Cell Death Differ. 2002. PMID: 12181739
-
XIAP: a potential determinant of ovarian follicular fate.Reproduction. 2012 Aug;144(2):165-76. doi: 10.1530/REP-12-0142. Epub 2012 May 31. Reproduction. 2012. PMID: 22653317 Review.
Cited by
-
Tobacco nicotine promotes TRAIL resistance in lung cancer through SNHG5.Exp Ther Med. 2023 Feb 10;25(3):131. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.11830. eCollection 2023 Mar. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 36845946 Free PMC article.
-
Killing by Degradation: Regulation of Apoptosis by the Ubiquitin-Proteasome-System.Cells. 2021 Dec 8;10(12):3465. doi: 10.3390/cells10123465. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34943974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
lncRNA WT1-AS attenuates hypoxia/ischemia-induced neuronal injury during cerebral ischemic stroke via miR-186-5p/XIAP axis.Open Med (Wars). 2022 Jul 25;17(1):1338-1349. doi: 10.1515/med-2022-0528. eCollection 2022. Open Med (Wars). 2022. PMID: 35959150 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted Evaluation of Inhibitors of Anti-Apoptotic Proteins in Head and Neck Cancer: Insights from In Vitro, In Vivo, and Clinical Studies (Review).Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Sep 30;17(10):1308. doi: 10.3390/ph17101308. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39458950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester: Unveiling its potential as a potent apoptosis inducer for combating hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Oncol Rep. 2024 Feb;51(2):21. doi: 10.3892/or.2023.8680. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Oncol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38099422 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duckett C.S., Nava V.E., Gedrich R.W., Clem R.J., Van Dongen J.L., Gilfillan M.C., Shiels H., Hardwick J.M., Thompson C.B. A conserved family of cellular genes related to the baculovirus iap gene and encoding apoptosis inhibitors. EMBO J. 1996;15:2685–2694. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1996.tb00629.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- UniProtKB-Q6PIA0 (Q6PIA0_HUMAN) [(accessed on 29 October 2020)]; Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q6PIA0//URL.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

