TLR9 Binding to Beclin 1 and Mitochondrial SIRT3 by a Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitor Protects the Heart from Doxorubicin Toxicity
- PMID: 33138323
- PMCID: PMC7693736
- DOI: 10.3390/biology9110369
TLR9 Binding to Beclin 1 and Mitochondrial SIRT3 by a Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitor Protects the Heart from Doxorubicin Toxicity
Abstract
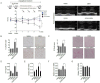
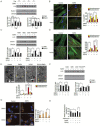
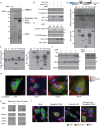
Large cardiovascular outcome trials have reported favorable effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on heart failure. To study the potential mechanism of the SGLT2 inhibition in heart failure, we used the murine doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy model and identified the toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9), NAD-dependent deacetylase sirtuin-3 (SIRT3), and Beclin 1, acting in a complex together in response to empagliflozin treatment. The interactions and implications in mitochondrial function were evaluated with TLR9 deficient, SIRT3 deficient, Beclin 1 haplodeficient, and autophagy reporter mice and confirmed in a patient with SIRT3 point mutation and reduced enzymatic activity. The SGLT2 inhibitor, empagliflozin, protects the heart from doxorubicin cardiomyopathy in mice, by acting through a novel Beclin 1-toll-like receptor (TLR) 9-sirtuin-(SIRT) 3 axis. TLR9 and SIRT3 were both essential for the protective effects of empagliflozin. The dilated cardiomyopathy patient with SIRT3 point mutation and reduced enzymatic activity is associated with reduced TLR9 activation and the absence of mitochondrial responses in the heart after the SGLT2 inhibitor treatment. Our data indicate a dynamic communication between autophagy and Beclin 1-TLR9-SIRT3 complexes in the mitochondria in response to empagliflozin that may serve as a potential treatment strategy for heart failure.
Keywords: Beclin 1; SGLT2 inhibitor; SIRT3; TLR9; doxorubicin; empagliflozin; heart failure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Honokiol, an activator of Sirtuin-3 (SIRT3) preserves mitochondria and protects the heart from doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy in mice.Oncotarget. 2017 May 23;8(21):34082-34098. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16133. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28423723 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioprotective Potential of an SGLT2 Inhibitor Against Doxorubicin-Induced Heart Failure.Korean Circ J. 2019 Dec;49(12):1183-1195. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2019.0180. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Korean Circ J. 2019. PMID: 31456369 Free PMC article.
-
Sirt3 confers protection against neuronal ischemia by inducing autophagy: Involvement of the AMPK-mTOR pathway.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Jul;108:345-353. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.04.005. Epub 2017 Apr 7. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28396174
-
Autophagy-dependent and -independent modulation of oxidative and organellar stress in the diabetic heart by glucose-lowering drugs.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 May 13;19(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01041-4. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 32404204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Empagliflozin Prevents Worsening of Cardiac Function in an Experimental Model of Pressure Overload-Induced Heart Failure.JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2017 Aug 4;2(4):347-354. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2017.07.003. eCollection 2017 Aug. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2017. PMID: 30062155 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors on Cardiac Protection.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 2;22(13):7170. doi: 10.3390/ijms22137170. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34281221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SGLT2 inhibitor promotes mitochondrial dysfunction and ER-phagy in colorectal cancer cells.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 May 29;29(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00599-1. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38811901 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Work as a "Regulator" of Autophagic Activity in Overnutrition Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 21;12:761842. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.761842. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34744742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Current State of Research on Sirtuin-Mediated Autophagy in Cardiovascular Diseases.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023 Sep 6;10(9):382. doi: 10.3390/jcdd10090382. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023. PMID: 37754811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors protect tissues via cellular and mitochondrial pathways: Experimental and clinical evidence.World J Exp Med. 2024 Jun 20;14(2):91519. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v14.i2.91519. eCollection 2024 Jun 20. World J Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38948421 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Castagno D., Baird-Gunning J., Jhund P.S., Zoccai G.B., Macdonald M.R., Petrie M.C., Gaita F., McMurray J.J. Intensive glycemic control has no impact on the risk of heart failure in type 2 diabetic patients: Evidence from a 37,229 patient meta-analysis. Am. Heart J. 2011;162:938.e2–948.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2011.07.030. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boussageon R., Bejan-Angoulvant T., Saadatian-Elahi M., Lafont S., Bergeonneau C., Kassaï B., Erpeldinger S., Wright J.M., Gueyffier F., Cornu C. Effect of intensive glucose lowering treatment on all cause mortality, cardiovascular death, and microvascular events in type 2 diabetes: Meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2011;343:d4169. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d4169. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

