Study of spatiotemporal liquid dynamics in a vibrating vocal fold by using a self-oscillating poroelastic model
- PMID: 33138511
- PMCID: PMC7575330
- DOI: 10.1121/10.0002163
Study of spatiotemporal liquid dynamics in a vibrating vocal fold by using a self-oscillating poroelastic model
Abstract
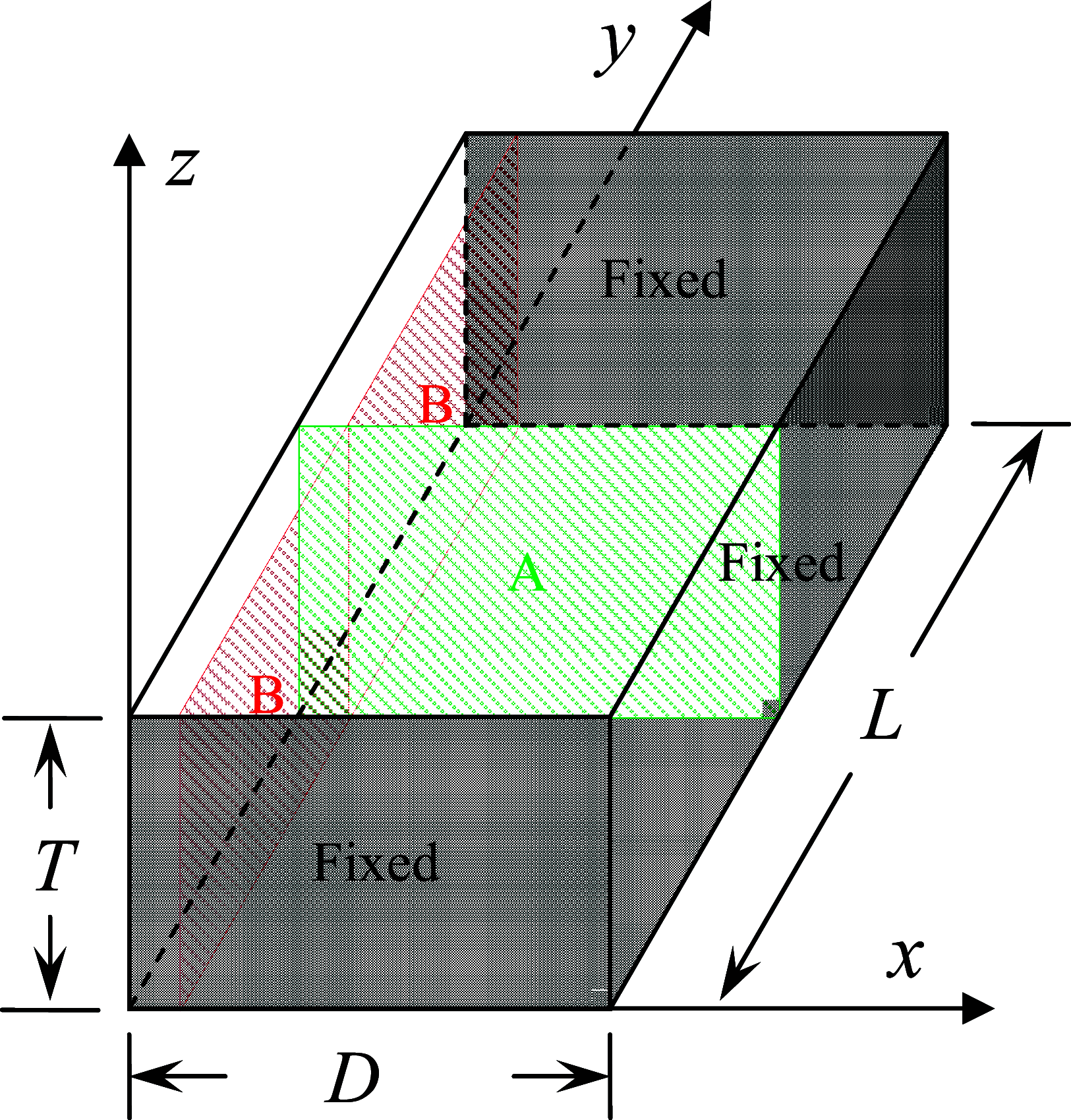
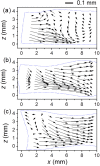
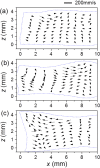
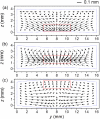
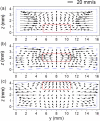
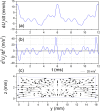
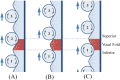
The main purpose of this study is to investigate the spatiotemporal interstitial fluid dynamics in a vibrating vocal fold. A self-oscillating poroelastic model is proposed to study the liquid dynamics in the vibrating vocal folds by treating the vocal fold tissue as a transversally isotropic, fluid-saturated, porous material. Rich spatiotemporal liquid dynamics have been found. Specifically, in the vertical direction, the liquid is transported from the inferior side to the superior side due to the propagation of the mucosal wave. In the longitudinal direction, the liquid accumulates at the anterior-posterior midpoint. However, the contact between the two vocal folds forces the accumulated liquid out laterally in a very short time span. These findings could be helpful for exploring etiology of some laryngeal pathologies, optimizing laryngeal disease treatment, and understanding hemodynamics in the vocal folds.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of poroelastic coefficients on normal vibration modes in vocal-fold tissues.J Acoust Soc Am. 2011 Feb;129(2):934-43. doi: 10.1121/1.3533692. J Acoust Soc Am. 2011. PMID: 21361450
-
A fluid-saturated poroelastic model of the vocal folds with hydrated tissue.J Biomech. 2009 Apr 16;42(6):774-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2008.12.006. Epub 2009 Mar 5. J Biomech. 2009. PMID: 19268294 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid accumulation in vibrating vocal fold tissue: a simplified model based on a fluid-saturated porous solid theory.J Voice. 2010 May;24(3):260-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2008.09.005. Epub 2009 Aug 5. J Voice. 2010. PMID: 19660905 Free PMC article.
-
Vocal fold dynamics for frequency change.J Voice. 2014 Jul;28(4):395-405. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2013.12.005. Epub 2014 Apr 13. J Voice. 2014. PMID: 24726331 Review.
-
Mechanical characterization of vocal fold tissue: a review study.J Voice. 2014 Nov;28(6):657-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2014.03.001. Epub 2014 Jul 5. J Voice. 2014. PMID: 25008382 Review.
Cited by
-
Biophysical aspects of mechanotransduction in cells and their physiological/biological implications in vocal fold vibration: a narrative review.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jan 27;13:1501341. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1501341. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 39931244 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

