Disparities in case frequency and mortality of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) among various states in the United States
- PMID: 33138653
- PMCID: PMC7877922
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2020.1840620
Disparities in case frequency and mortality of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) among various states in the United States
Abstract
Objective: To utilize publicly reported, state-level data to identify factors associated with the frequency of cases, tests, and mortality in the USA.
Materials and methods: Retrospective study using publicly reported data collected included the number of COVID-19 cases, tests and mortality from March 14th through April 30th. Publicly available state-level data was collected which included: demographics comorbidities, state characteristics and environmental factors. Univariate and multivariate regression analyses were performed to identify the significantly associated factors with percent mortality, case and testing frequency. All analyses were state-level analyses and not patient-level analyses.
Results: A total of 1,090,500 COVID-19 cases were reported during the study period. The calculated case and testing frequency were 3332 and 19,193 per 1,000,000 patients. There were 63,642 deaths during this period which resulted in a mortality of 5.8%. Factors including to but not limited to population density (beta coefficient 7.5, p < .01), transportation volume (beta coefficient 0.1, p < .01), tourism index (beta coefficient -0.1, p = .02) and older age (beta coefficient 0.2, p = .01) are associated with case frequency and percent mortality.
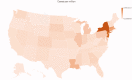
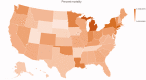
Conclusions: There were wide variations in testing and case frequencies of COVID-19 among different states in the US. States with higher population density had a higher case and testing rate. States with larger population of elderly and higher tourism had a higher mortality. Key messages There were wide variations in testing and case frequencies of COVID-19 among different states in the USA. States with higher population density had a higher case and testing rate. States with larger population of elderly and higher tourism had a higher mortality.
Keywords: COVID-19; climate; coronavirus; epidemiology; risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease 2019. (COVID-19) Pandemic. 2020; https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019. Accessed May 3, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous