Long non-coding RNA H19 deficiency ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis
- PMID: 33138822
- PMCID: PMC7607673
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-020-01534-6
Long non-coding RNA H19 deficiency ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis
Abstract
Background: The poor understanding of pathogenesis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) impaired development of effective therapeutic strategies. The aim of the current study is to investigate the roles of long non-coding RNA H19 (lncRNA H19) in the pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis of IPF.
Methods: Bleomycin was used to induce pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in mice. The mRNAs and proteins expression in lung tissues was determined by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and western blot. H19 knockout (H19-/-) mice were generated by CRISPR/Cas9.
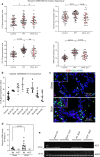
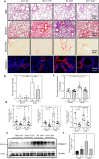
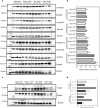
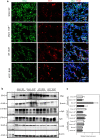
Results: The expression of H19 mRNA was up-regulated in fibrotic lungs patients with IPF as well as in lungs tissues that obtained from bleomycin-treated mice. H19-/- mice suppressed bleomycin-mediated pulmonary inflammation and inhibited the Il6/Stat3 signaling. H19 deficiency ameliorated bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis and repressed the activation of TGF-β/Smad and S1pr2/Sphk2 in the lungs of bleomycin-treated mice.
Conclusions: Our data suggests that H19 is a profibrotic lncRNA and a potential therapeutic target for IPF.
Keywords: Pulmonary fibrosis; S1pr2; Smad; lncRNA H19.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Travis WD, Costabel U, Hansell DM, King TE, Jr, Lynch DA, Nicholson AG, Ryerson CJ, Ryu JH, Selman M, Wells AU, et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: update of the international multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;188:733–748. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201308-1483ST. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

