DNA hydroxymethylation is associated with disease severity and persists at enhancers of oncogenic regions in multiple myeloma
- PMID: 33138842
- PMCID: PMC7607866
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-020-00953-y
DNA hydroxymethylation is associated with disease severity and persists at enhancers of oncogenic regions in multiple myeloma
Abstract
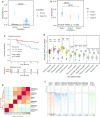
Background: Multiple myeloma (MM) is a heterogeneous plasma cell malignancy that remains challenging to cure. Global hypomethylation correlates with an aggressive phenotype of the disease, while hypermethylation is observed at particular regions of myeloma such as B cell-specific enhancers. The recently discovered active epigenetic mark 5-hydroxymethylCytosine (5hmC) may also play a role in tumor biology; however, little is known about its level and distribution in myeloma. In this study, we investigated the global level and the genomic localization of 5hmC in myeloma cells from 40 newly diagnosed patients, including paired relapses, and of control individuals.
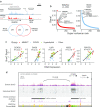
Results: Compared to normal plasma cells, we found global 5hmC levels to be lower in myeloma (P < 0.001). Higher levels of 5hmC were found in lower grades of the International Staging System prognostic index (P < 0.05) and tend to associate with a longer overall survival (P < 0.1). From the hydroxymethylome data, we observed that the remaining 5hmC is organized in large domains overlapping with active chromatin marks and chromatin opening. We discovered that 5hmC strongly persists at key oncogenic genes such as CCND1, CCND2 and MMSET and characterized domains that are specifically hydroxymethylated in myeloma subgroups. Novel 5hmC-enriched domains were found at putative enhancers of CCND2 and MYC in newly diagnosed patients.
Conclusions: 5hmC level is associated with clinical aspects of MM. Mapping 5hmC at a genome-wide level provides insights into the disease biology directly from genomic DNA, which makes it a potent mark to study epigenetics on large patient cohorts.
Keywords: DNA modifications; Epigenetics; Hydroxymethylation; Multiple myeloma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chromatin-based, in cis and in trans regulatory rewiring underpins distinct oncogenic transcriptomes in multiple myeloma.Nat Commun. 2021 Sep 14;12(1):5450. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25704-2. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34521827 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related epigenome-wide DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation in longitudinal mouse blood.Epigenetics. 2018;13(7):779-792. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2018.1507198. Epub 2018 Aug 23. Epigenetics. 2018. PMID: 30079798 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental Epigenetics and Genome Flexibility: Focus on 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 2;21(9):3223. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093223. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32370155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The functional epigenetic landscape of aberrant gene expression in molecular subgroups of newly diagnosed multiple myeloma.J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Aug 6;13(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00933-y. J Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32762714 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxymethylation and tumors: can 5-hydroxymethylation be used as a marker for tumor diagnosis and treatment?Hum Genomics. 2020 May 6;14(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s40246-020-00265-5. Hum Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32375881 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-omics tumor profiling technologies to develop precision medicine in multiple myeloma.Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2021;2(1):65-106. doi: 10.37349/etat.2021.00034. Epub 2021 Feb 28. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2021. PMID: 36046090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spectroscopic and in vitro Investigations of Fe2+ /α-Ketoglutarate-Dependent Enzymes Involved in Nucleic Acid Repair and Modification.Chembiochem. 2022 Jun 3;23(11):e202100605. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202100605. Epub 2022 Feb 15. Chembiochem. 2022. PMID: 35040547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic Uracil and Aberrant Profile of Demethylation Intermediates in Epigenetics and Hematologic Malignancies.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 19;22(8):4212. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084212. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33921666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome Instability in Multiple Myeloma: Facts and Factors.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 26;13(23):5949. doi: 10.3390/cancers13235949. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34885058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting gene expression state and prioritizing putative enhancers using 5hmC signal.Genome Biol. 2024 Jun 3;25(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s13059-024-03273-z. Genome Biol. 2024. PMID: 38825692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moreau P, Attal M, Hulin C, et al. Bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone with or without daratumumab before and after autologous stem-cell transplantation for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (CASSIOPEIA): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. The Lancet. 2019;394(10192):29–38. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31240-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

