Protein phase separation and its role in tumorigenesis
- PMID: 33138914
- PMCID: PMC7609067
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.60264
Protein phase separation and its role in tumorigenesis
Abstract
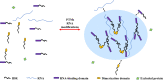
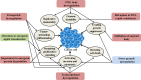
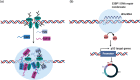
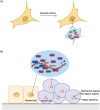
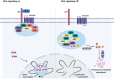
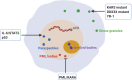
Cancer is a disease characterized by uncontrolled cell proliferation, but the precise pathological mechanisms underlying tumorigenesis often remain to be elucidated. In recent years, condensates formed by phase separation have emerged as a new principle governing the organization and functional regulation of cells. Increasing evidence links cancer-related mutations to aberrantly altered condensate assembly, suggesting that condensates play a key role in tumorigenesis. In this review, we summarize and discuss the latest progress on the formation, regulation, and function of condensates. Special emphasis is given to emerging evidence regarding the link between condensates and the initiation and progression of cancers.
Keywords: C. elegans; E. coli; S. cerevisiae; biomolecular condensate; cancer; cancer biology; human; membraneless organelle; mouse; phase separation.
© 2020, Jiang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
SJ, JF, CC, BL No competing interests declared, SA is a scientific advisor of Dewpoint Therapeutics
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liquid‒liquid phase separation: roles and implications in future cancer treatment.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Aug 6;19(13):4139-4156. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.81521. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37705755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomolecular Condensates and Their Links to Cancer Progression.Trends Biochem Sci. 2021 Jul;46(7):535-549. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2021.01.002. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Trends Biochem Sci. 2021. PMID: 33579564 Review.
-
Liquid-liquid phase separation in subcellular assemblages and signaling pathways: Chromatin modifications induced gene regulation for cellular physiology and functions including carcinogenesis.Biochimie. 2024 Aug;223:74-97. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2024.05.007. Epub 2024 May 7. Biochimie. 2024. PMID: 38723938 Review.
-
Biomolecular condensates: A new lens on cancer biology.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2025 Feb;1880(1):189245. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2024.189245. Epub 2024 Dec 13. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39675392 Review.
-
Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation in Disease.Annu Rev Genet. 2019 Dec 3;53:171-194. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-112618-043527. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Annu Rev Genet. 2019. PMID: 31430179 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular insights into the effect of 1,6-hexanediol on FUS phase separation.EMBO J. 2025 May;44(10):2725-2740. doi: 10.1038/s44318-025-00431-2. Epub 2025 Apr 25. EMBO J. 2025. PMID: 40281357 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin balances cell redox and energy homeostasis.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2023 Nov 28;16(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s13072-023-00520-8. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2023. PMID: 38017471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of ESRP2 Activates TAK1-MAPK Signaling through the Fetal RNA-Splicing Program to Promote Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Jan;11(1):e2305653. doi: 10.1002/advs.202305653. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 37985644 Free PMC article.
-
From the Catastrophic Objective Irreproducibility of Cancer Research and Unavoidable Failures of Molecular Targeted Therapies to the Sparkling Hope of Supramolecular Targeted Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 1;24(3):2796. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032796. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomolecular condensates in cancer biology.Cancer Sci. 2022 Feb;113(2):382-391. doi: 10.1111/cas.15232. Epub 2021 Dec 14. Cancer Sci. 2022. PMID: 34865286 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adriaens C, Standaert L, Barra J, Latil M, Verfaillie A, Kalev P, Boeckx B, Wijnhoven PW, Radaelli E, Vermi W, Leucci E, Lapouge G, Beck B, van den Oord J, Nakagawa S, Hirose T, Sablina AA, Lambrechts D, Aerts S, Blanpain C, Marine JC. p53 induces formation of NEAT1 lncRNA-containing paraspeckles that modulate replication stress response and chemosensitivity. Nature Medicine. 2016;22:861–868. doi: 10.1038/nm.4135. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

