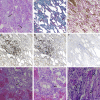
Eosinophilic pulmonary vasculitis as a manifestation of the hyperinflammatory phase of COVID-19
- PMID: 33139059
- PMCID: PMC7587128
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.09.026
Eosinophilic pulmonary vasculitis as a manifestation of the hyperinflammatory phase of COVID-19
Figures
Comment on
-
Eosinophil responses during COVID-19 infections and coronavirus vaccination.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020 Jul;146(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.021. Epub 2020 Apr 25. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32344056 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

