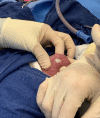
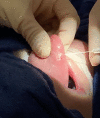
Treatment of tongue telangiectasia in a patient with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia
- PMID: 33139375
- PMCID: PMC7607586
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2020-238485
Treatment of tongue telangiectasia in a patient with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia
Abstract
A 61-year-old Caucasian woman presented to an outpatient otolaryngology clinic with increased bleeding from a dorsal tongue telangiectasia for 3 weeks. Her history was significant for hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT), a rare condition that causes vascular dysplasia, and recent symptomatic anaemia requiring blood transfusions. After failing medical management with topical haemostatic agents, she was offered and underwent surgical intervention to remove the tongue telangiectasia with duel therapy potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP) laser coblation and bevacizumab injections. A team of otolaryngologists removed the lesion without complications, and the patient denied bleeding, had minimal pain, and endorsed increased quality of life postoperatively. Tongue telangiectasias can cause life-threatening bleeding in some patients with HHT, and no surgical management guidelines exist to treat them. This case demonstrates the efficacy of KTP laser followed by bevacizumab injections in treating tongue telangiectasias in a patient with HHT.
Keywords: ear; head and neck surgery; nose and throat; nose and throat/otolaryngology; otolaryngology / ENT; therapeutic indications.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2020. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Masuda Y, Tanabe T, Ohmae Y, et al. Using the KTP laser to control epistaxis in patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Pract Otorhinolaryngol 2004;97:1075–81. 10.5631/jibirin.97.1075 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous