Early life of Neanderthals
- PMID: 33139541
- PMCID: PMC7682388
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2011765117
Early life of Neanderthals
Abstract
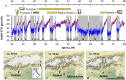
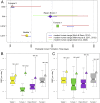
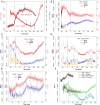
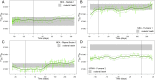
The early onset of weaning in modern humans has been linked to the high nutritional demand of brain development that is intimately connected with infant physiology and growth rate. In Neanderthals, ontogenetic patterns in early life are still debated, with some studies suggesting an accelerated development and others indicating only subtle differences vs. modern humans. Here we report the onset of weaning and rates of enamel growth using an unprecedented sample set of three late (∼70 to 50 ka) Neanderthals and one Upper Paleolithic modern human from northeastern Italy via spatially resolved chemical/isotopic analyses and histomorphometry of deciduous teeth. Our results reveal that the modern human nursing strategy, with onset of weaning at 5 to 6 mo, was present among these Neanderthals. This evidence, combined with dental development akin to modern humans, highlights their similar metabolic constraints during early life and excludes late weaning as a factor contributing to Neanderthals' demise.
Keywords: Neanderthal ontogeny; dental histology; life histories; nursing strategy; spatially resolved chemical analyses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sellen D. W., Evolution of infant and young child feeding: Implications for contemporary public health. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 27, 123–148 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Kennedy G. E., From the ape’s dilemma to the weanling’s dilemma: Early weaning and its evolutionary context. J. Hum. Evol. 48, 123–145 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Humphrey L. T., Weaning behaviour in human evolution. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 21, 453–461 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Davies D. P., O’Hare B., Weaning: A worry as old as time. Curr. Paediatr. 14, 83–96 (2004).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

