In situ sprayed NIR-responsive, analgesic black phosphorus-based gel for diabetic ulcer treatment
- PMID: 33139557
- PMCID: PMC7682336
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2016268117
In situ sprayed NIR-responsive, analgesic black phosphorus-based gel for diabetic ulcer treatment
Abstract
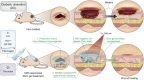
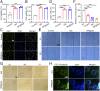
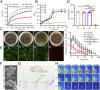
The treatment of diabetic ulcer (DU) remains a major clinical challenge due to the complex wound-healing milieu that features chronic wounds, impaired angiogenesis, persistent pain, bacterial infection, and exacerbated inflammation. A strategy that effectively targets all these issues has proven elusive. Herein, we use a smart black phosphorus (BP)-based gel with the characteristics of rapid formation and near-infrared light (NIR) responsiveness to address these problems. The in situ sprayed BP-based gel could act as 1) a temporary, biomimetic "skin" to temporarily shield the tissue from the external environment and accelerate chronic wound healing by promoting the proliferation of endothelial cells, vascularization, and angiogenesis and 2) a drug "reservoir" to store therapeutic BP and pain-relieving lidocaine hydrochloride (Lid). Within several minutes of NIR laser irradiation, the BP-based gel generates local heat to accelerate microcirculatory blood flow, mediate the release of loaded Lid for "on-demand" pain relief, eliminate bacteria, and reduce inflammation. Therefore, our study not only introduces a concept of in situ sprayed, NIR-responsive pain relief gel targeting the challenging wound-healing milieu in diabetes but also provides a proof-of-concept application of BP-based materials in DU treatment.
Keywords: analgesic; black phosphorus; diabetic ulcer; fibrin gel; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

